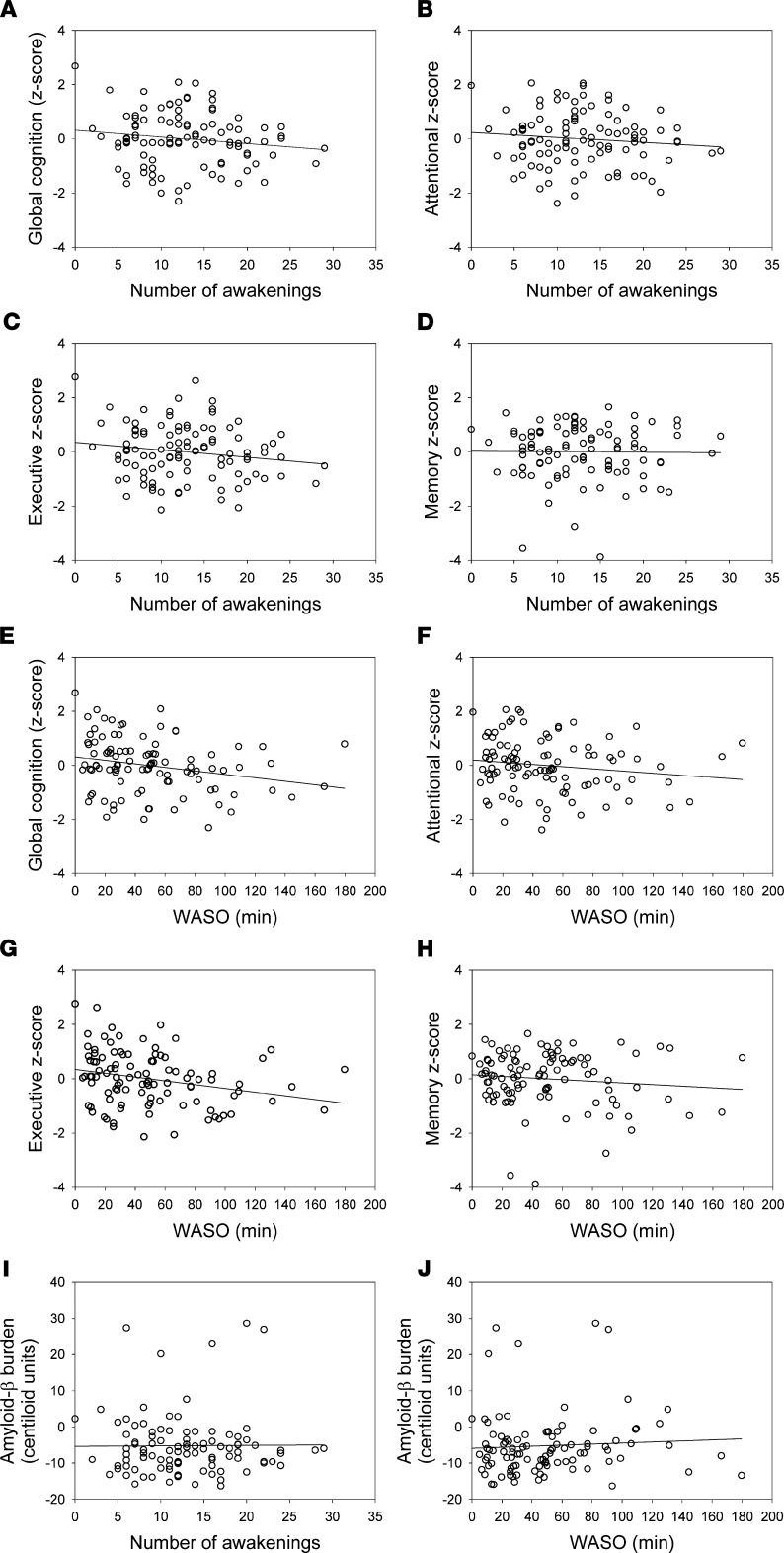
Figure 5. Association between number of awakenings and cognition.
(A) Global cognitive performance (Spearman’s r = –0.10, P = 0.30; GLMM F1,95 = 2.21, P = 0.14); (B) attentional (Spearman’s r = –0.07, P = 0.48; GLMM F1,95 = 0.89, P = 0.35); (C) executive (Spearman’s r = –0.11, P = 0.25; GLMM F1,95 = 3.53, P = 0.06); (D) memory performances (Spearman’s r = –0.03, P = 0.80; GLMM F1,95 = 0.00, P = 0.98); (E) between WASO and cognition global cognitive performance (Spearman’s r = –0.24, P = 0.01; GLMM F1,95 = 4.66, P = 0.03); (F) attentional (Spearman’s r = –0.17, P = 0.11;GLMM: F1,95 = 0.56, P = 0.46); (G) executive (Spearman’s r = –0.28, P = 0.005;GLMM: F1,95 = 7.58, P = 0.007); (H) memory performances (Spearman’s r = –0.06, P = 0.59; GLMM: F1,95 = 1.11, P = 0.30); (I) between early cortical Aβ burden and number of awakenings (Spearman’s r = 0.01, P = 0.90; GLMM F1,95 = 0.22, P = 0.64); and (J) WASO (Spearman’s r = 0.11, P = 0.28; GLMM F1,95 = 0.05, P = 0.83).