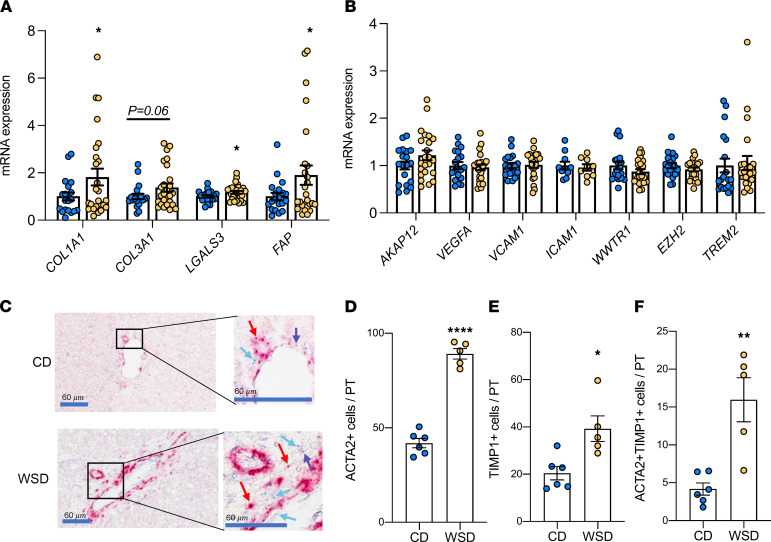
Figure 2. Evidence for increased collagen synthesis and stellate cell activation in NHP WSD-exposed fetal liver.
Expression of genes in CD (blue) and WSD (yellow) fetal liver tissue associated with collagen synthesis and stellate cell activation (A). ANOVA with fixed effect for maternal diet is significant for all variables shown (P < 0.1). Individual post test comparisons were performed between CD and WSD; n = 20 CD and n = 26 WSD. *P < 0.05. (B) Expression of genes associated with endothelial dysfunction, the YAP/TAZ pathway, and myeloid cell inflammation; n = 20 CD and n = 26 WSD. (C) Representative images and zooms of portal triads of CD- and WSD-exposed fetal livers via RNAscope. Red arrows indicate ACTA2+ cells; blue arrows indicate TIMP1+ cells; purple arrows indicate ACTA2 and TIMP1 double-positive cells. Scale bar: 60 μm (boxed areas are enlarged and cropped on the right). Average numbers of ACTA2+ cells (D), TIMP1+ cells (E), and ACTA2 and TIMP1 double-positive cells (F) per portal triad (PT) via RNAscope; n = 6 CD and n = 5 WSD. Unpaired 2-tailed Student’s t test was used to test significance. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ****P < 0.0005.