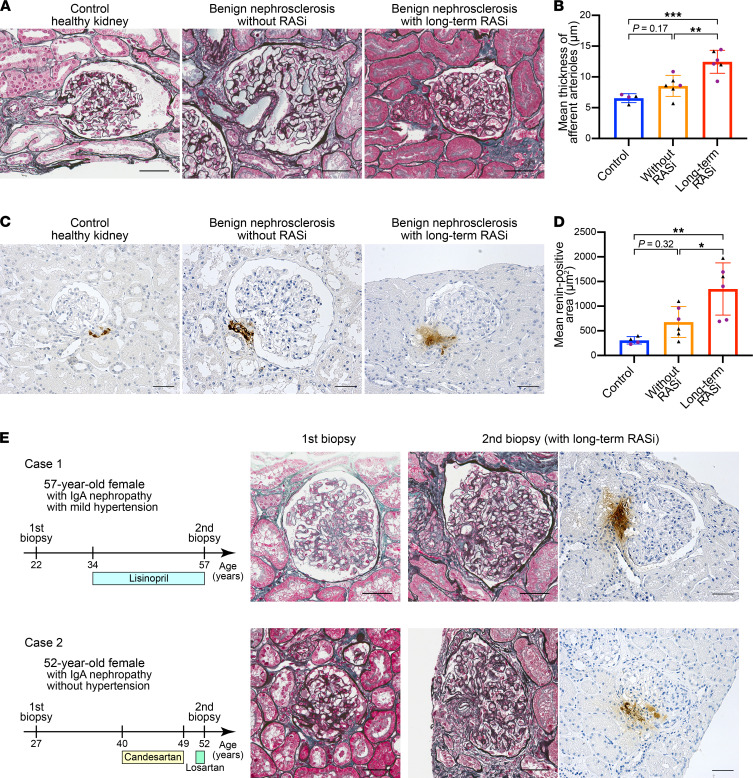
Figure 8. Long-term inhibition of RAS induces arteriolar hypertrophy in human patients.
(A) Representative images of periodic acid–methenamine silver (PAM) with Masson’s trichrome staining of kidney sections from healthy control individuals, patients with benign nephrosclerosis without RASi, and patients with benign nephrosclerosis with long-term usage of RASi. Patients with long-term usage of RASi showed marked hypertrophy in afferent arterioles. (B) Mean thickness of afferent arterioles at the JG area. Patients with long-term usage of RASi (n = 6) showed significantly thicker renal arteriolar walls compared with controls (n = 4) and patients with nephrosclerosis without RASi (n = 6) (1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test). (C) Representative images of immunohistochemistry for renin in kidney sections. Patients with long-term usage of RASi showed extensive renin-positive regions in the JG area. (D) Mean renin-positive area at the JG area. Patients with long-term usage of RASi (n = 6) showed significantly larger areas compared with controls (n = 4) and patients with nephrosclerosis without RASi (n = 6) (1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test). (E) Patients with long-term RASi with mild or no hypertension. Patient 1 was a 57-year-old female with IgAN. She was diagnosed with IgAN by her first renal biopsy and administered lisinopril (ACEi) for 23 years before her second renal biopsy. Patient 2 was a 52-year-old female with IgAN. She was diagnosed with IgAN by her first renal biopsy and administered candesartan (ARB) for 9 years. After 2 years of self-interruption, she received losartan (ARB) for 1 year before her second renal biopsy. Both patients had no abnormalities in afferent arterioles at their first biopsies and showed marked afferent arteriolar hypertrophy at the second renal biopsies. Scale bars: 50 μm. All data are reported as means ± standard deviation. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. ACEi, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin II receptor blocker; JG, juxtaglomerular; IgAN, IgA nephropathy; RAS, renin-angiotensin system; RASi, renin-angiotensin system inhibitor.