Figure 3.
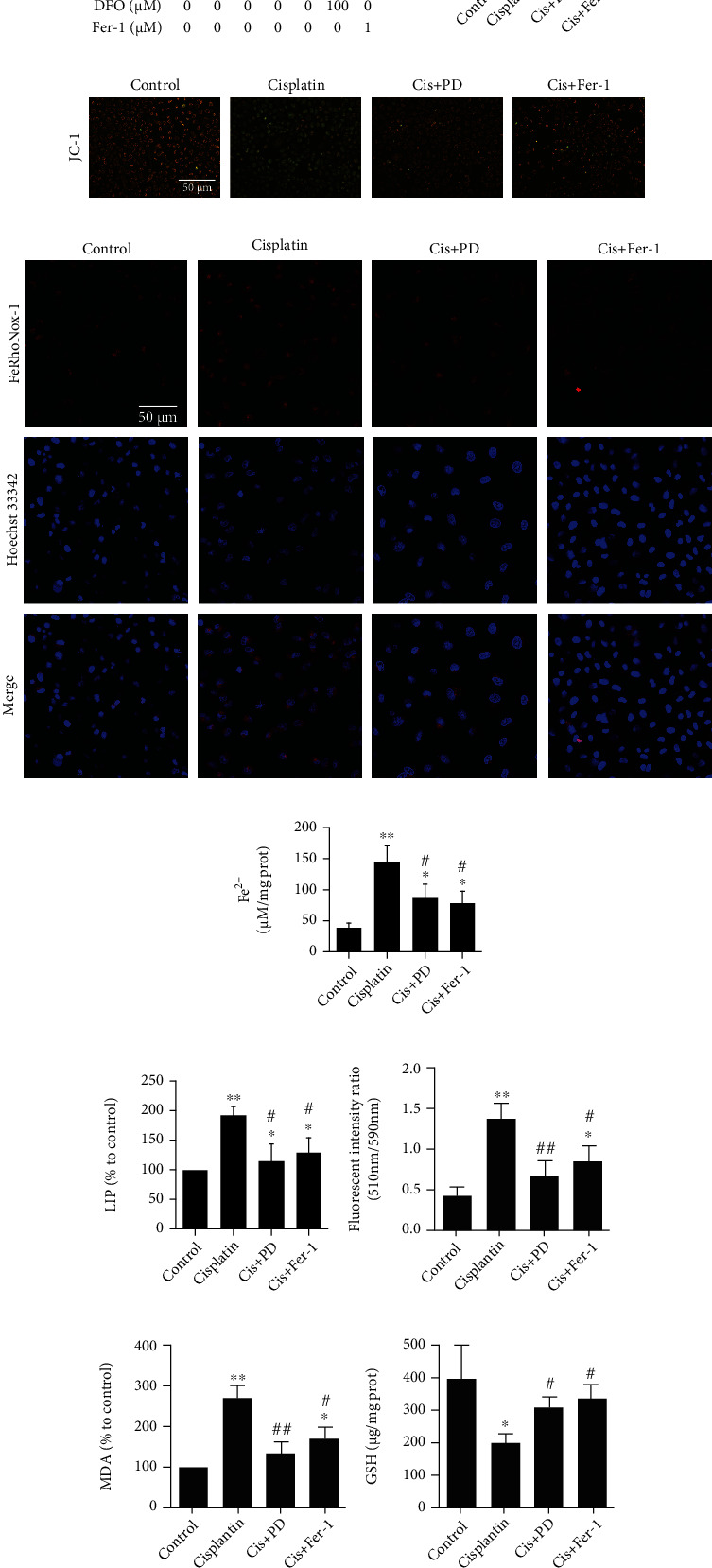
Inhibition of PD on cisplatin-induced ferroptosis in HK-2 cells. (a) CCK8 showing the viability of HK-2 cells under the treatment of different concentration of PD (10, 20, and 40 μM), DFO (100 μM), or Fer-1 (1 μM) in presence or absence of erastin (20 μM). (b) CCK8 showing the viability of HK-2 cells under the simultaneous treatment of different concentration of cisplatin for 24 h. (c) CCK8 showing the viability of HK-2 cells under the treatment of different concentration of PD (10, 20, and 40 μM), DFO (100 μM), or Fer-1 (1 μM) with or without cisplatin (20 μM). (d, e) Changes in MMP expression levels were detected by fluorescence microscope and flow cytometry using JC-1. (f–h) Intracellular labile iron in HK-2 cells was measured using selective Fe (II) fluorescent probe FeRhoNox-1, iron assay kit, and LIP assay. (i, j) The lipid peroxidation in HK-2 cells was measured using C11-BODIPY581/591 and MDA assay. (k, l) The level of GSH and the GPx4 activity of HK-2 cells were examined in 24 h after cisplatin injection. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01 vs. control (nondrug treated); #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. cisplatin (or erastin) alone; $P < 0.05, $$P < 0.01 vs. Cis (or erastin)+40 μM PD (n = 6). Cis: cisplatin; PD: polydatin; Fer-1: ferrostatin-1; DFO: deferoxamine; LIP: labile iron pool; MDA: malondialdehyde; GSH: glutathione; GPx4: glutathione peroxidase-4.
