Fig. 2.
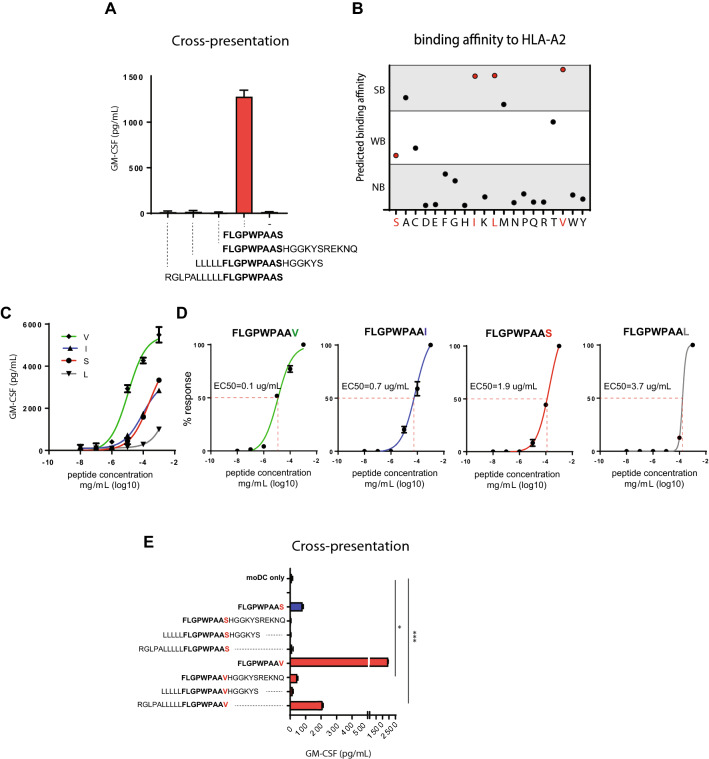
Amino acid replacements at the C-terminus of the LRPAP1 signal peptide. a Long peptides of the LRPAP1 epitope FLGPWPAAS were incubated with monocyte-derived dendritic cells and examined for cross-presentation with TEIPP-specific CD8 T cell clone 1A8. Natural flanking amino acids were used to elongate the minimal epitope. Exogenous pulsing with short peptide was used as positive control. b Predicted HLA-A*0201 binding affinity scores of LRPAP1 peptides with substituted amino acids at the C-terminal p9 (netMHC 4.1 algorithm). Each dot represents one peptide. Strong binder (SB, < 50 nM), weak binder (WB, 50 < 500 nM), non-binder (NB, > 500 nM), see Supplementary Table 1 for exact values and ranking. Red dots represent the peptide variants included in the follow-up experiments. c Functional T cell avidity was estimated by activation of LRPAP121–30-specific T cell clone. The LRPAP1 short peptide variants were pulsed on HLA-A*0201 EBV-JY B cells in serial dilutions of the peptides. d EC50 values were calculated from values obtained in C. e Long peptides of the S- and V- variants of the LRPAP1 sequence were incubated with monocyte-derived dendritic cells and examined for cross-presentation with TEIPP-specific T cell clone 1A8. Pulsed short peptide served as positive controls. Means with SD are plotted from a representative experiment (n = 3)