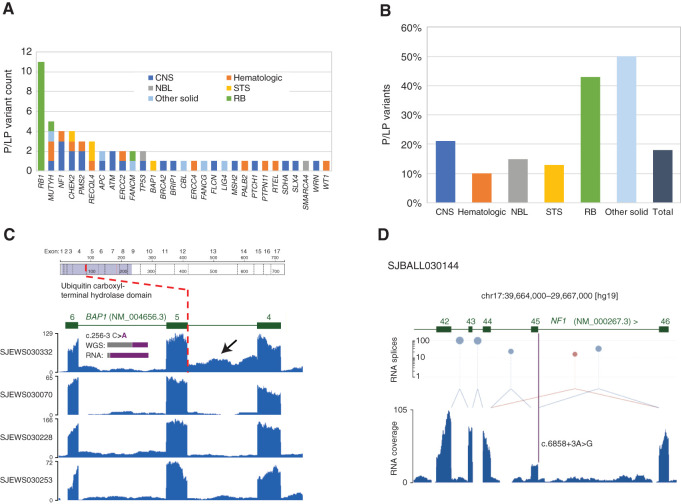
Figure 4.
Germline variants and assessment of variant pathogenicity based on RNA data. A, Numbers of germline P/LP variants, broken down by gene and tumor type. NBL, neuroblastoma; RB, retinoblastoma. B, Proportions of germline P/LP variants, broken down by tumor type. C,BAP1 intron 4 retention in SJEWS030332 compared to other G4K Ewing sarcoma cases. Each blue histogram shows hg19-aligned RNA-seq coverage relative to the BAP1 gene model in green (note that BAP1 is on the negative strand). The position of the exon 5 splice acceptor mutation is indicated by the red dotted line. Increased read coverage in the SJEWS030332 (bearing a mutation at the -3 position of exon 5) intron relative to the three other samples indicates intron 4 retention (black arrow). Inset histograms show the relative proportion of reference and variant alleles in tumor-derived WGS and RNA-seq in gray and purple, respectively. Corresponding read counts are WGS: 32G/21T (40% variant allele) and RNA 2G/28T (93% variant allele). Above the RNA coverage plots is a schematic of the BAP1 protein with the location of the splice variant leading to protein truncation marked. D,NF1 exon 45 skipping in SJBALL030144. The blue histogram shows RNA-seq coverage relative to the NF1 gene model in green. Canonical splices are shown as light blue links between exons, and a noncanonical splice is shown in mauve. The height of mauve and blue lollipops is proportional to the number of splice junction reads detected plotted on a log scale on the y-axis. The purple bar indicates the position of the NF1 exon 45 splice acceptor mutation. Exon 45 expression is diminished relative to flanking exons, and a noncanonical splice linking exons 44 and 46 is observed, indicating an exon skipping event.