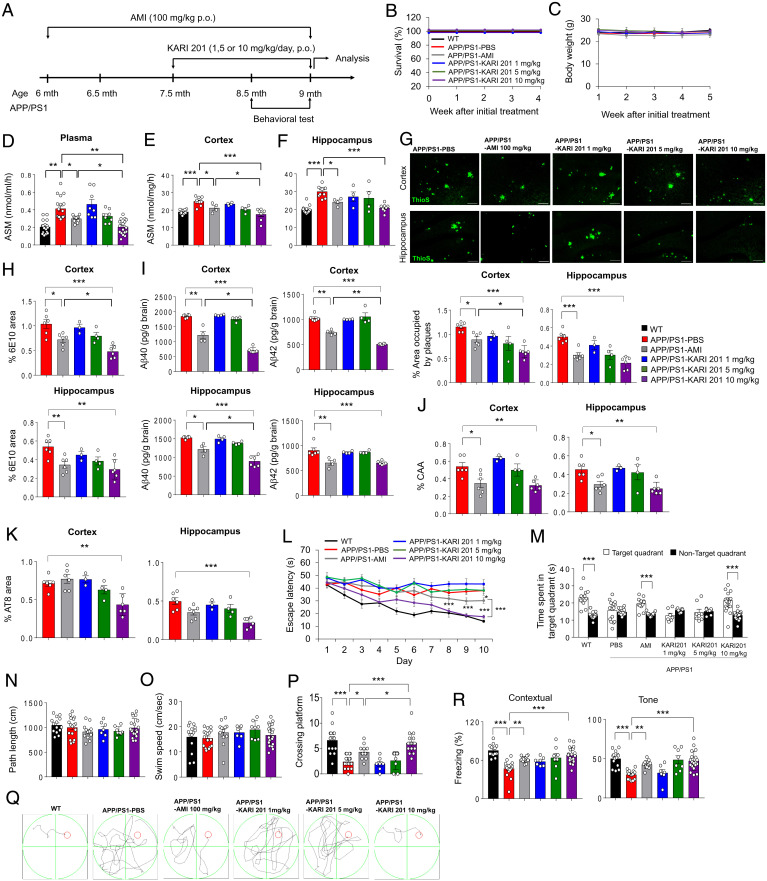
Fig. 2.
Administration of KARI 201 reduces amyloid pathology and restores cognitive impairment in APP/PS1 mice. (A) Scheme of experimental procedures. (B and C) Survival (B) and body weight (C) during oral administration (p.o., per os) of each compound (n = 8 to 12 mice per group). (D–F) ASM activity in plasma (D; n = 8 to 18 mice per group), cortex (E; n = 4 to 11 mice per group), and hippocampus (F; n = 4 to 11 mice per group) of each group. (G, Top) Representative immunofluorescence images of thioflavin S (ThioS, Aβ plaques) in each group. (Scale bars, 100 μm.) (G, Bottom) Quantification of the area occupied by Aβ plaques (n = 3 to 6 mice per group). (H) Quantification of 6E10 (n = 3 to 6 mice per group). (I) Analysis of Aβ40 and Aβ42 depositions using ELISA kits (n = 4 to 6 mice per group). (J and K) Quantification of amyloid angiopathy (J; n = 3 to 6 mice per group; CAA) and tau hyperphosphorylation (K; n = 3 to 6 mice per group; AT8). (L) Learning and memory were assessed by the Morris water maze test (n = 7 to 19 mice per group). (M–O) At probe trial day 11, time spent on target platform (M), path length (N), and swim speed (O) were analyzed. (P) The number of times each animal entered the small target zone during the 60-s probe trial. (Q) Representative swimming paths at day 10 of training (n = 7 to 19 mice per group). (R) The results of contextual and tone tasks during fear-conditioning test (n = 7 to 19 mice per group). (D–P and R) One-way ANOVA, Tukey’s post hoc test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. All error bars indicate SEM. All data analysis was done in 9-mo-old mice.