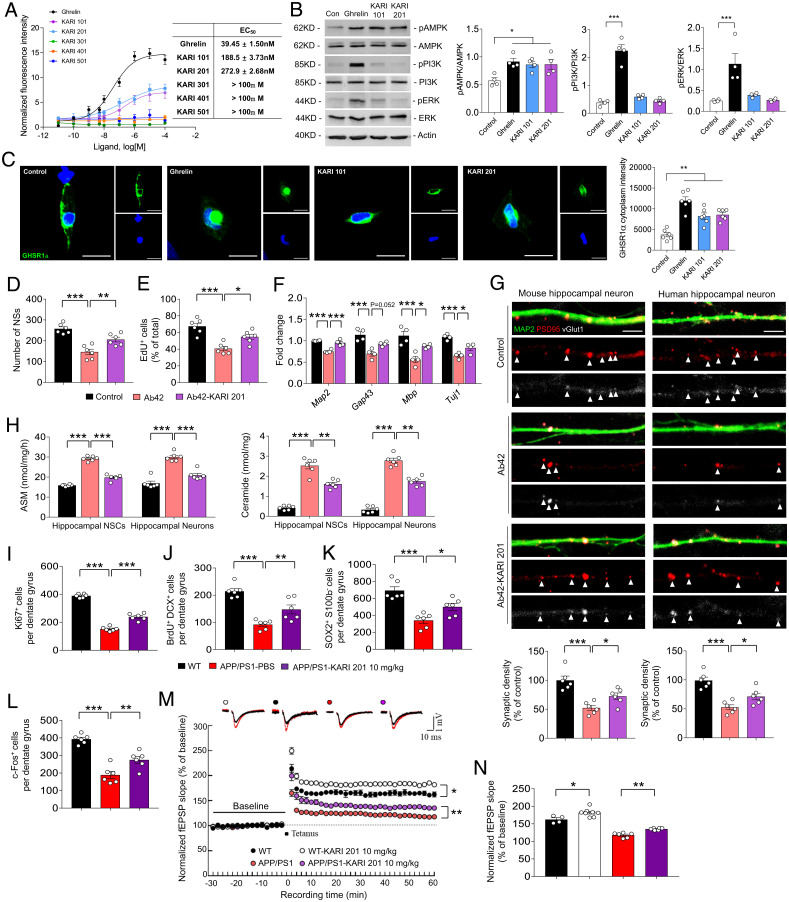
Fig. 5.
KARI 201 is a ghrelin receptor agonist and improves hippocampal neurogenesis and synapse plasticity. (A) Effect of various concentrations of the KARI compounds and ghrelin on Ca2+ mobilization in HEK293 cells transiently transfected with the WT human GhrR (data are mean ± SEM; n = 3 independent experiments). (B) Western blot analyses and quantification of pAMPK, APMK, pPI3K, PI3K, pERK, and ERK in ghrelin (10 µM), KARI 101 (10 µM), or KARI 201 (10 µM) treatment (n = 4 per group). (C) Immunocytochemistry of the ghrelin receptor (n = 6 per group). (Scale bars, 20 μm.) (D and E) Number of neurospheres (NSs) (D) and EdU-positive NSCs (E) in Aβ42 (1 µM, 24 h) treatment with or without KARI 201 (n = 6 per group). (F) qRT-PCR analysis of neuronal survival gene expression (n = 4 per group). (G) Effect of KARI 201 treatments on synaptic density in mouse hippocampal neurons in the presence or absence of Aβ42. Quantification and representative images of synapse staining. vGlut1 (white) and PSD95 (red) were used to visualize pre- and postsynaptic terminals, respectively. The dendrites were stained with MAP2 (green). The overlaid staining of vGlut1/PSD95 identifies synapses (n = 6 per group). (Scale bars, 5 μm.) (H) ASM activity and ceramide production in NSCs and neurons in Aβ42 treatment with or without KARI 201 (n = 6 per group). (I–K) The number of Ki67+ cells (I, proliferating cells), BrdU+/DCX+ cells (J, new neuroblasts), and SOX2+/S100β− cells (K, NSCs) in dentate gyrus of each mouse (n = 6 mice per group). (L) The number of c-Fos+ neurons in dentate gyrus of each mouse (n = 6 mice per group). (M and N) LTP induced by HFS (WT, n = 4; WT/KARI 201, 10 mg⋅kg−1, n = 8; APP/PS1/PBS, n = 4 to 6; APP/PS1/KARI 201, 10 mg⋅kg−1, n = 6). (B–N) One-way ANOVA, Tukey’s post hoc test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. All error bars indicate SEM. All data analysis was done in 9-mo-old mice.