Fig. 1.
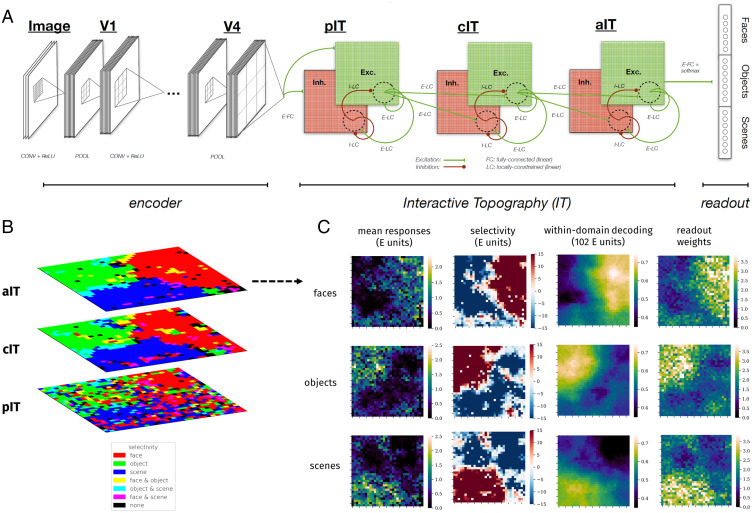
The interactive topographic network produces hierarchical domain-level organization. (A) Diagram of the ITN. An ITN model consists of three components: an encoder that approximates early visual processing prior to inferotemporal cortex, the IT areas that approximate inferotemporal cortex, and the readout mechanism for tasks such as object, scene, and face recognition. The architecture of each component is flexible. For example, a four-layer simple convolutional network or a deep 50-layer ResNet can be used as the encoder; whereas the former facilitates end-to-end training along with a temporally precise IT model, the latter supports better learning of the features that discriminate among trained categories. In this work, topographic organization is restricted to the IT layers. Shown is the main version of the ITN containing three constraints: a spatial connectivity cost pressuring local connectivity, separation of neurons with excitatory and inhibitory influences, and the restriction that all between-area connections are sent by the excitatory neurons. The final IT layer projects to the category readout layer containing one localist unit per learned category, here shown organized into three learned domains. (Note that this organization is merely visual and does not indicate any architectural segregation in the model.) (B) Domain selectivity at each level of the IT hierarchy. Selectivity is computed separately for each domain and then binarized by including all units corresponding to P < 0.001. Each domain is assigned a color channel to plot all selectivities simultaneously. Note that a unit can have zero, one, or two selective domains, but not three, as indicated in the color key. (C) Detailed investigation of domain-level topography in aIT. Each heatmap plots a metric for each unit in aIT. Left column shows the mean domain response for each domain, Center Left column shows domain selectivity, Center Right column shows the within-domain searchlight decoding accuracy, and Right column shows the mean of weights of a given aIT unit into the readout categories of a given domain.