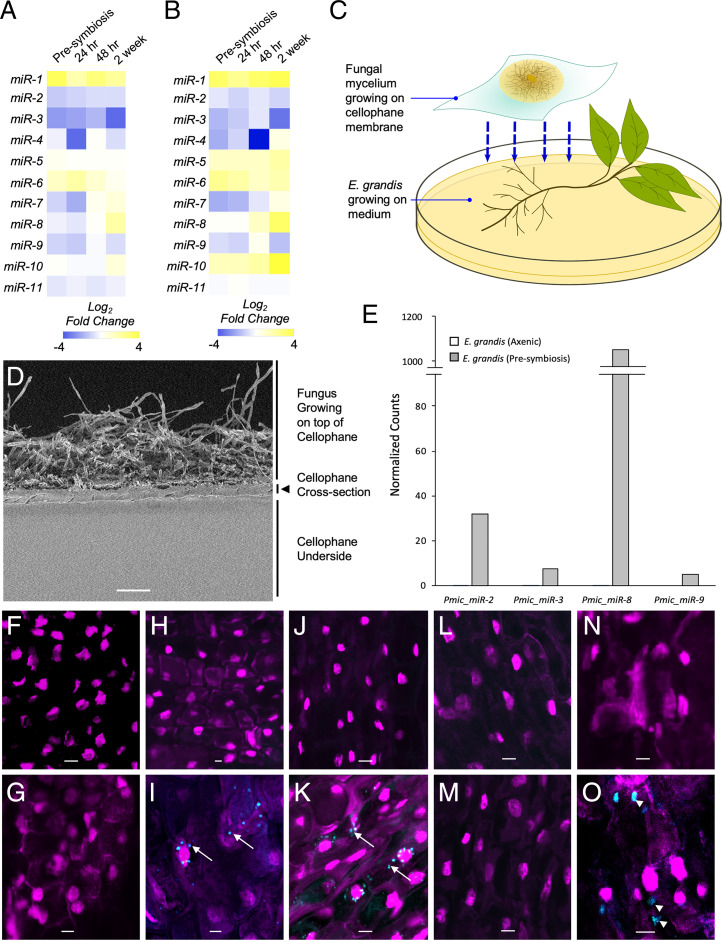
Fig. 1.
P. microcarpus miRNAs are differentially regulated during ECM symbiosis developments with E. grandis roots certain of which can be recovered and localized in the cells of E. grandis. Heatmaps showing the fold change in expression of the 11 predicted fungal miRNAs in P. microcarpus isolate SI14 (A) and isolate SI9 (B) across a time course of colonization with E. grandis roots. The color scale represents the normalized Log2 fold change of each miRNA at each timepoint of colonization compared to axenically grown fungal cultures (n = 3 to 4). (C) Diagram of Petri dish setup for presymbiotic exposure of the two organisms. The fungus is grown on top of a cellophane membrane and then transferred to rest over top of E. grandis roots. (D) Scanning electron micrograph of a cross-section of the cellophane membrane utilized, showing microscopic pores running throughout the material. (Scale bar, 40 μm.) (E) Bar graph depicting normalized read counts of four putative fungal miRNAs detected in E. grandis roots after presymbiotic interaction with P. microcarpus (presymbiosis; gray bars) but below detection limit in sRNA-seq libraries of E. grandis axenically grown roots where no fungus is present (axenic; white bars; see also SI Appendix, Fig. S3 for verification of results by qPCR). (F–O) ISH localization of Pmic_miR-8 in E. grandis root cells and controls using either a fluorescent anti-Pmic_miR-8 or scrambled sequence probe (blue signal in images) whereby the nuclei of root cells were visualized with propidium iodide (magenta signal in images). The specific treatments are as follows: probe-free ISH of presymbiotic roots (F); ISH of Pmic_miR-8 in E. grandis cells grown axenically (G); ISH of presymbiotic roots using a scrambled probe (H); ISH of presymbiotic roots using a Pmic_miR-8 probe with a positive signal for the target found in punctate structures within the cell (arrows) as well as more diffusely throughout the cell (I); ISH of presymbiotic roots treated with RNase prior to fixation to remove any RNA adherent to the cell surface and then probed with a scrambled probe (J); ISH of presymbiotic roots treated with RNase prior to fixation using a Pmic_miR-8 probe with a positive signal for the target found in punctate structures within the cell (arrows) (K); ISH with a scrambled probe of presymbiotic roots treated with RNase prior to, and post, fixation to remove any RNA adherent to the cell surface and within the cell postpermeabilization (L); ISH of presymbiotic roots treated with RNase prior to, and post, fixation to remove any RNA adherent to the cell surface and within the cell postpermeabilization and then probed with a Pmic_miR-8 probe (M); ISH of presymbiotic roots treated to induce plasmolysis using a scrambled probe (N); and ISH of presymbiotic roots treated to induce plasmolysis using a Pmic_miR-8 probe with a positive signal for the target found in larger concentrations within the cell (arrow head) (O). All images were acquired using an inverted Leica TCS SP5 laser-scanning confocal microscope with the same settings. (Scale bar, 20 µm for F–O.) All images are representative of four biological replicates.