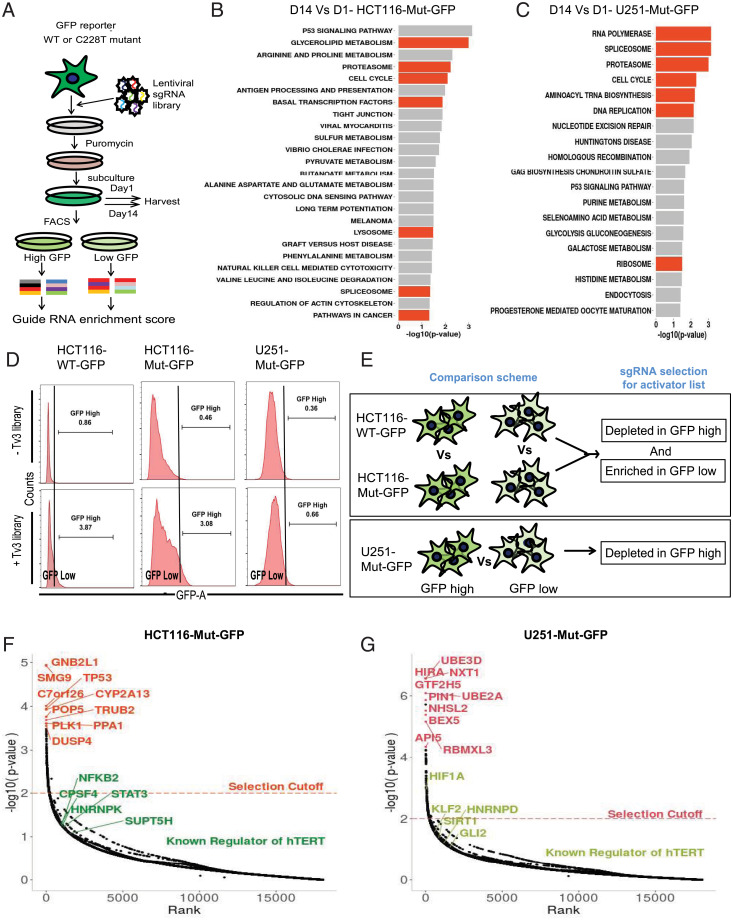
Fig. 4.
CRISPR knockout screen in GFP reporter cell lines. (A) Workflow for CRISPR knockout screen. The GFP reporter lines were transduced with lentiviral encoded sgRNA library and selected with puromycin. GFP sorting was done on day 14 to segregate GFP high and low populations for calculating sgRNA enrichment score. (B and C) Enriched KEGG pathways for depleted (negative selected) sgRNA from reporter cells at day 14 compared to day 1. The sgRNA targeting important cell survival pathways (orange bars) were depleted in both HCT116-Mut-GFP (B) and U251-Mut-GFP (C) cells at day 14. (D) Representative FACS histograms of GFP sorted reporter cells (HCT116 WT-GFP, Left; HCT116-Mut-GFP, Middle; U251-Mut-GFP, Right) before and after Tv3 sgRNA library expression. The population with high GFP fluorescence was sorted as GFP high, while the remaining populations were sorted into GFP low for subsequent genomic DNA isolation to look for sgRNA enrichment in the populations. (E) Schematic showing the comparison scheme for sorted cells to find activators of hTERT. For activators in HCT116 isogenic reporter lines HCT116-WT-GFP and HCT116-Mut-GFP, the comparison was made between the same populations of either GFP high or GFP low to look for depleted or enriched sgRNA targeting genes, respectively. For the nonisogenic line (U251-Mut-GFP), sgRNA depleted in GFP high Vs. GFP low was derived to look for negatively selected sgRNA in GFP high population. (F) Plot showing the P value distribution of sgRNA targeted genes and top hits of activator genes (orange) and known regulators of hTERT among all hits (green) identified from the HCT116-Mut-GFP cell line. (G) Plot showing the P value distribution of sgRNA targeted genes and top hits of activator genes (orange) and known regulators of hTERT among all hits (green) identified from U251-Mut-GFP cells line.