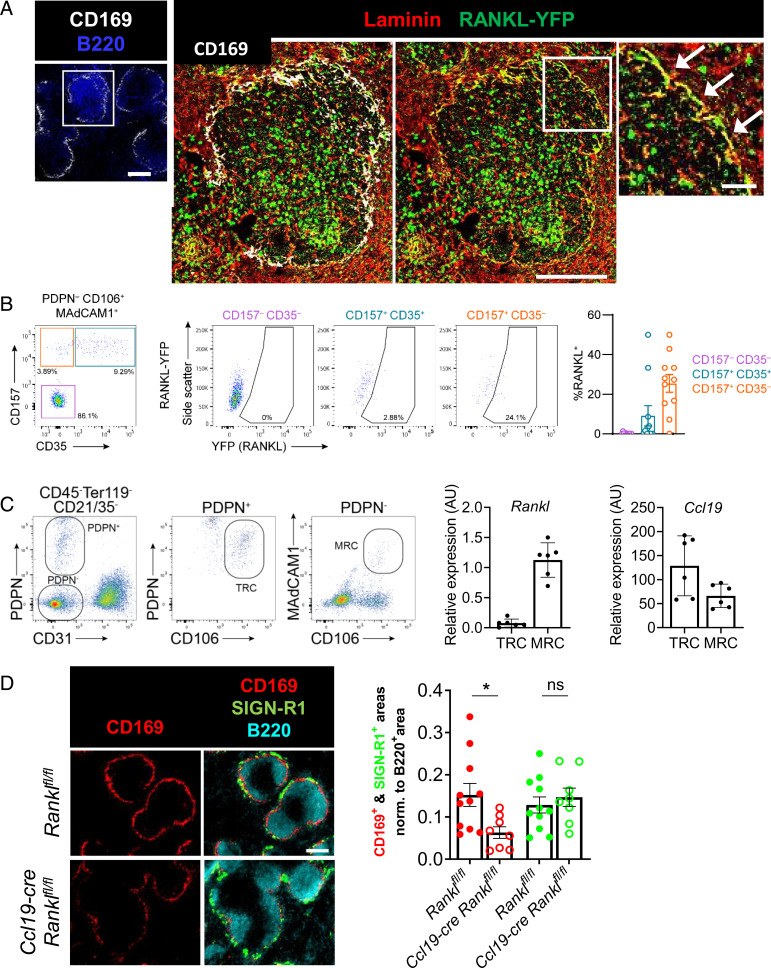
Fig. 4.
Splenic marginal reticular cells are a local source of RANKL for MMM differentiation. (A) Confocal microscopic images of spleen sections of RANKL reporter mice (RANKL-YFP) stained for YFP, CD169, B220, and laminin. The inset shows a higher magnification of RANKL-YFP–expressing laminin+ cells of the MZ. (B) Flow cytometry gating strategy to identify RANKL-YFP–expressing cells among the CD31− Pdpn− CD106/VCAM-1+ MAdCAM-1+ stromal cells. Cells with high YFP expression were found within the CD157+ CD35− population. The graph summarizes the percentage of RANKL-YFP+ among the indicated cell types. Data points represent independent analyses, n = 11 from three independent experiments. (C) Gating strategy to sort TRCs and MRCs. The relative transcriptional levels of Rankl and Ccl19 were assessed by RT-qPCR of the sorted cells. The data are from four independent experiments. (D) Wide-field immunofluorescence microscopic images of CD169, SIGN-R1, and B220 in Ccl19-cre Ranklfl/fl and Ranklfl/fl mice. Graph depicts the mean area of each macrophage marker with individual data points normalized to the B220+ area. Statistical significance (Mann-Whitney test); *P < 0.05; ns, not significant; error bar, SEM [scale bars, 100 μm (A, Left and Middle), 20 μm (A, Right), and 200 μm (D)].