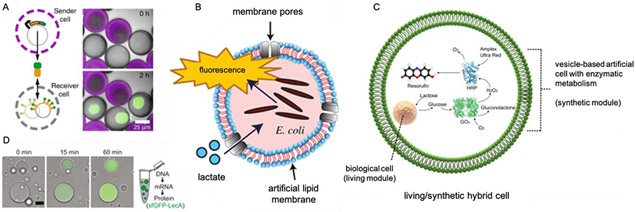
Figure 2: Synthetic organelles and communication.
A) A porous synthetic cell with a nucleus-like DNA-hydrogel that expresses display proteins and communicates with neighboring synthetic cell through protein diffusion [78]. B) encapsulated E. coli functions as lactate sensor in synthetic cell [69]. C) Internal lipid droplet with sponge morphology enables expression regulation and mimics interconnected membrane morphologies of Golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum [72]. D) internal synthetic cell chemistry communicating with encapsulated bacterial and eukaryotic cells to display logic gate encodable mutualism [68].