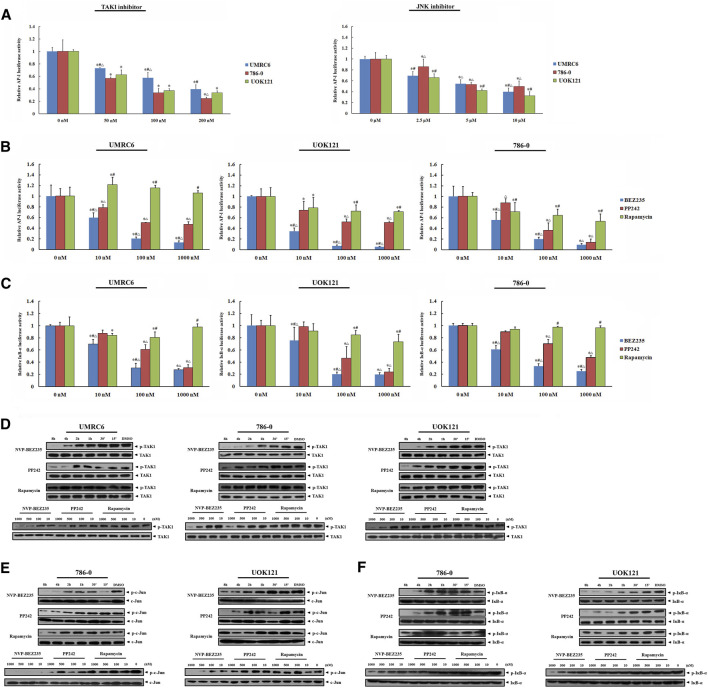
FIGURE 6.
Inhibition of JNK/AP-1 and IKK pathways via TAK1 in RCC cell lines by NVP-BEZ235 and PP242. (A) Effect of JNK or TAK1 inhibition on AP-1 transcriptional activity in RCC cells assessed by luciferase reporter assay. UMRC6, 786-0, and UOK121 cells were transfected with AP-1 reporter plasmid and a Renilla-luciferase control plasmid, followed by incubation with TAK1-inhibitor or JNK-inhibitor for 24 h. Untreated cells served as control (0 μM). The AP-1-dependent. firefly luciferase activity was normalized to the Renilla luciferase activity as a transfection control. Next, the transfected RCC cells were incubated with various concentrations (10, 100, 1,000 nM) of NVP-BEZ235, PP242, or Rapamycin for 24 h. The (B) AP-1 activity and (C) IκB-α activity were measured by the ratio of firefly luciferase activity to Renilla luciferase activity. DMSO-treated cells (0 nM) served as control. All value are means ± SD of three replicates. *p < 0.05, versus the corresponding control (0 nM) group; #p < 0.05, versus the corresponding PP242 group; ∆p < 0.05, versus the corresponding Rapamycin group. Western blot assay further confirmed the inhibition of (D) TAK1, (E) JNK, and (F) IKK activation. RCC cells were incubated with 10, 100, 500, 1,000 nM of NVP-BEZ235, PP242 and Rapamycin for 48h, or 200 nm of these compounds for the time courses as indicated. The relative phosphorylation levels of TAK1, c-Jun and IκB-α were calculated and normalized to total protein. Cells harvested at 0 h or DMSO-treated cells (0 nM) served as control. Results are representative of three independent experiments.