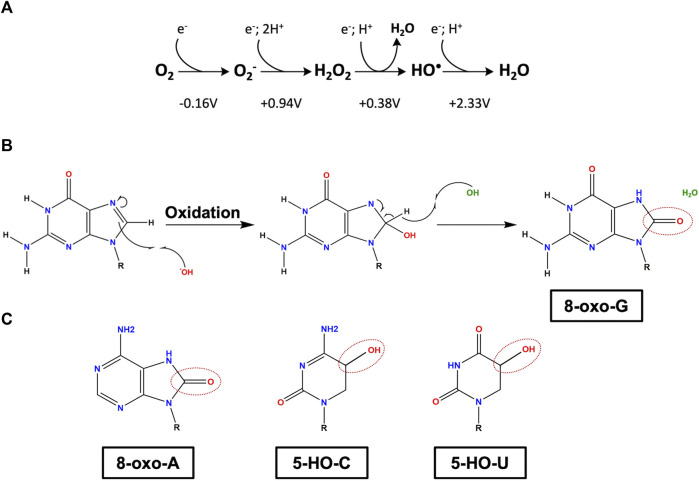
FIGURE 1.
Main oxidative lesions found in RNA. (A) Redox state of molecular oxygen. From left to right: molecular oxygen (O2), superoxide anion (O2 −), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), hydroxyl radical (HO•) and water (H2O). The reduction potentials are shown regarding the standard concentration of O2 to be 1M at pH 7 (adapted from Imlay 2009). (B) Reaction of a guanosine with a hydroxyl radical, yielding 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanosine (8-oxo-G). (C) Three modified RNA nucleobases: oxidized adenosine 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroadenosine (8-oxo-A), oxidized cytosine 5-hydroxycytosine (5-HO-C) and oxidized uridine 5-hydroxyuridine (5-HO-U). Oxidation sites are marked as dashed circles. R represents the ribose group.