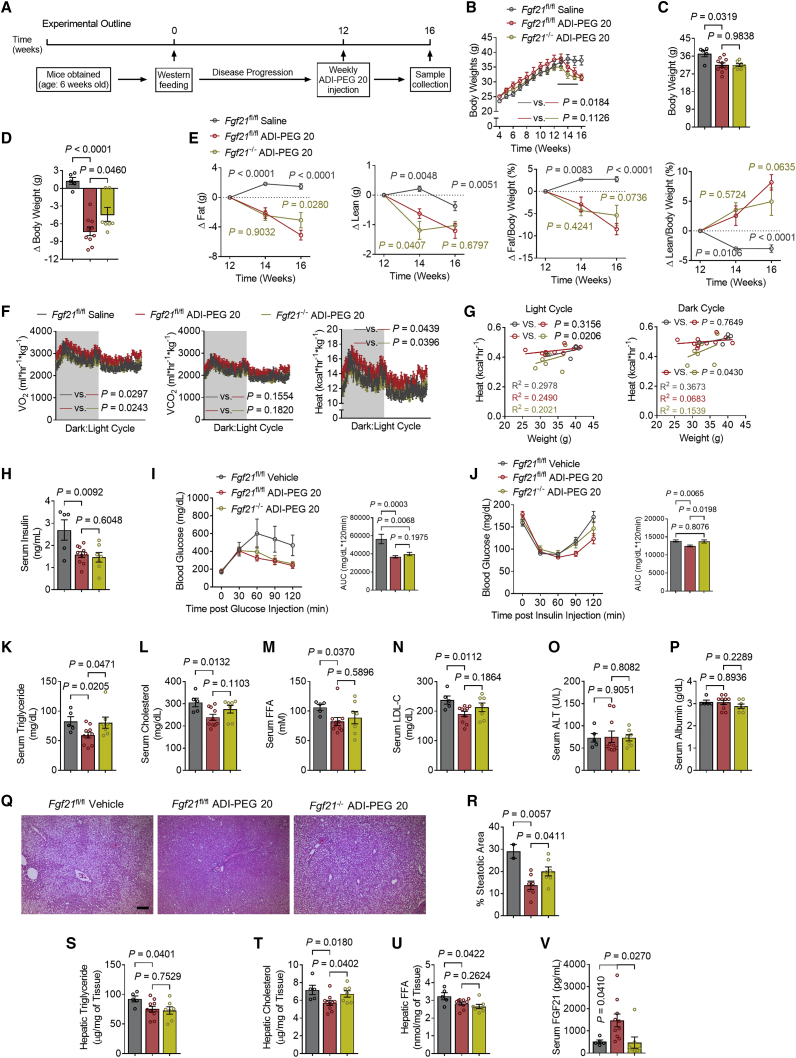
Figure 4.
Hepatic-specific Fgf21 knockout partially abolishes ADI-PEG 20-mediated therapeutic effects
(A) Schematic of experimental design used to test the role of ADI-PEG 20 in Fgf21 LKO WD-fed mice.
(B–E) Body weight over time (B), end point body weight (C), and change in body weight (D) of vehicle- and ADI-PEG 20-treated Fgf21 LKO mice (vehicle-treated Fgf21fl/fl mice, n = 5. ADI-PEG 20-treated Fgf21fl/fl mice, n = 10. ADI-PEG 20-treated Fgf21 LKO mice, n = 7).
(E) Change in body fat and lean composition.
(F) Whole-body oxygen consumption (VO2), carbon dioxide (VCO2), and energy expenditure during light and dark cycle (shaded area) in vehicle- and ADI-PEG 20-treated Fgf21 LKO mice.
(G) Body weight to energy expenditure regression test during light and dark cycle.
(H) Serum insulin in vehicle- and ADI-PEG 20-treated Fgf21 LKO mice.
(I and J) Intraperitoneal tolerance tests for glucose (GTT, I) and for glucose (ITT, J).
(K–N) Serum triglyceride (K), cholesterol (L), non-esterified fatty acid (M), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (N) in vehicle- and ADI-PEG 20-treated Fgf21 LKO mice.
(O and P) Serum ALT (O) and serum albumin (P) contents.
(Q and R) Liver sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E, Q) with steatotic area (e.g., aparenchymal space) quantified (R). Scale bars, 100 μm.
(S–U) Triglyceride (S), cholesterol (T), and non-esterified fatty acid (U) contents in the livers of vehicle- and ADI-PEG 20-treated Fgf21 LKO mice.
(V) Serum FGF21 content.
Data represented in mean ± SEM. Each data point represents an individual animal. Exact p values are shown. Statistical significance was determined using two-way ANOVA in (B), (E), (F), (I), and (J). Unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test was used in (C), (D), (H), (K)–(P), and (R)–(V).