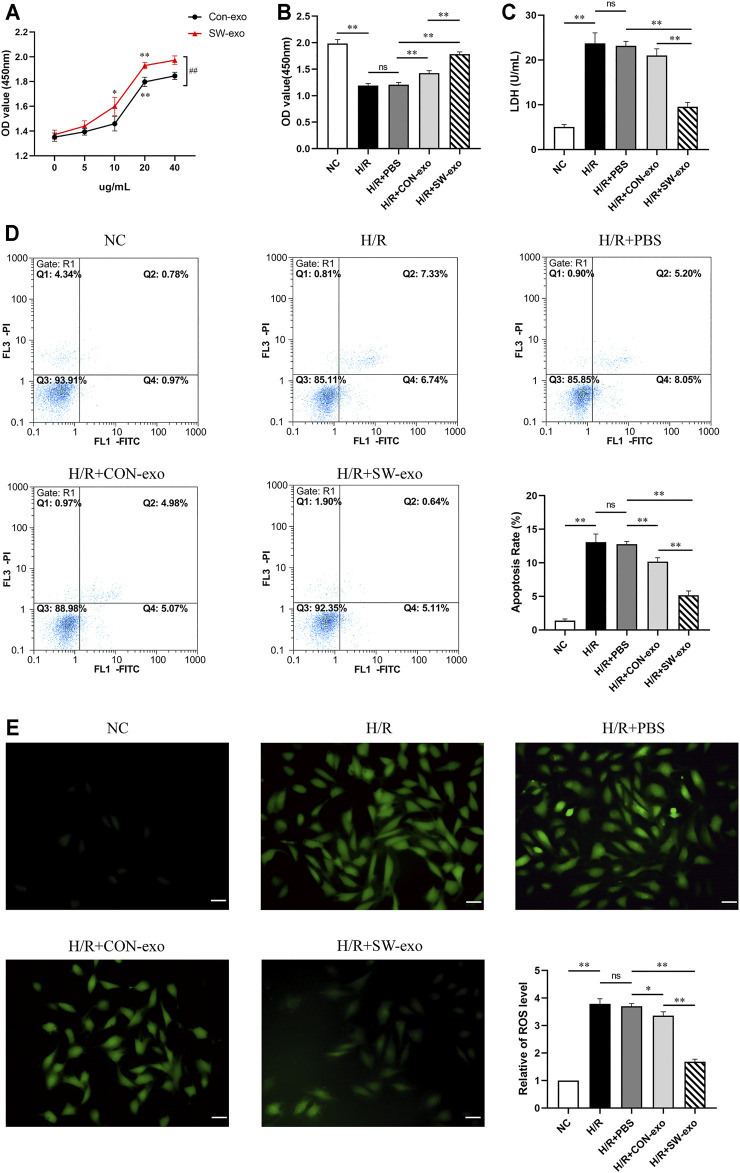
FIGURE 3.
Extracorporeal cardiac shock wave (ECSW)-induced ECFCs-exo protected cardiomyocytes against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury. (A) The cell viability of H9c2 cells after hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R) injury treated with CON-exo and SW-exo at different concentrations from 0 to 40 µg/ml. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, within group; ##p < 0.01, between groups. (B–E) Quantitative analysis of the cell viability (B) by cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity (C) by reagent kit, cell apoptosis rate (D) by flow cytometry, and the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) (E) by dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) staining were shown for each group, including NC, H/R, and H9c2 cells after H/R injury treated with PBS, CON-exo, and SW-exo. Data are presented as mean ± SD, n = 3. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, E: scale bar = 50 μm.