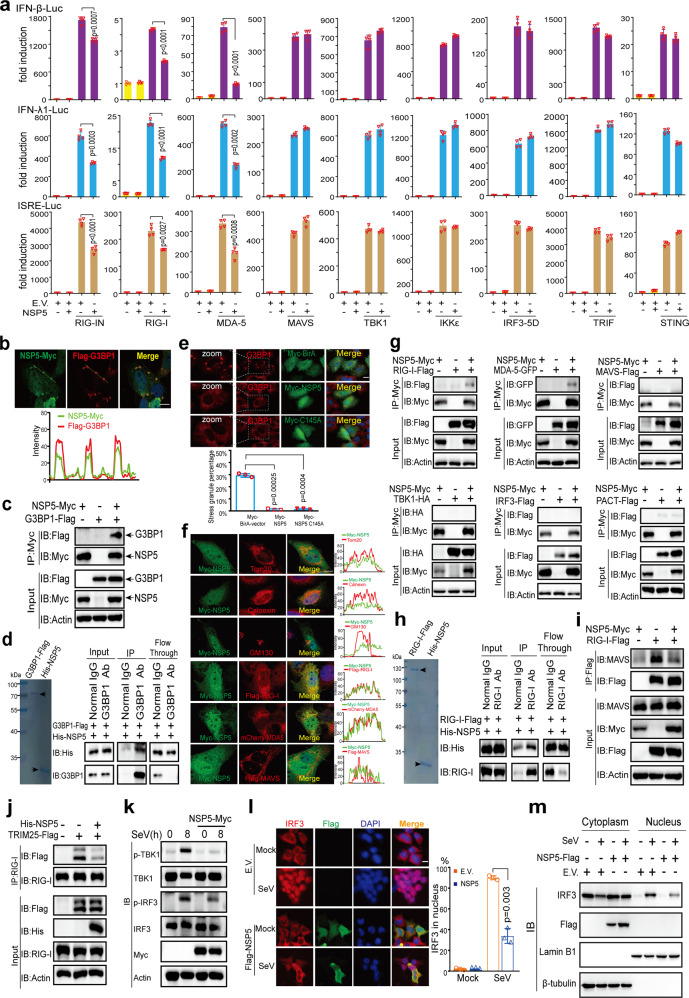
Fig. 4.
NSP5 inhibits RLR-induced IFN activation. a IFN-β, IFN-λ1, or ISRE luciferase reporters and protein-expressing plasmids were transfected into HEK293T cells as indicated. pRL-TK plasmid was transfected to normalize transfection efficiency. After transfection for 36 h, the cells were lysed to examine the luciferase activities by dual-luciferase assays. b NSP5 colocalizes with SG marker G3BP1. Top panel: Representative confocal images of NSP5-Myc colocalization with G3BP1-Flag in HeLa cells. Scale bar, 10 µm. Bottom panel: Line profiling of NSP5-Myc with G3BP1-Flag. The intensity of each line was measured by ImageJ software and drawn by GraphPad Prism 8.0. c Co-IP analysis of the interaction between NSP5-Myc and G3BP1-Flag in HEK293T cells. HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids for 24 h before co-IP with Myc antibody. Results shown are representative of two independent experiments. d NSP5 directly binds to G3BP1. Left panel: Coomassie blue staining analysis of the purified G3BP1-Flag and His-NSP5 proteins. Right panel: Co-IP analysis of the in vitro interaction between G3BP1-Flag and His-NSP5. e NSP5 inhibits SG formation induced by plasmid transfection. Top panel: Confocal microscopic analysis of SG formation in HeLa cells transfected with plasmids of Myc-BirA (control group), Myc-NSP5, or Myc-NSP5 C145A for 24 h. Scale bars, 10 μm. Bottom panel: Quantification analysis of the percentage of SG formation (50 cells per sample). f NSP5 colocalizes with RIG-I and MDA5. Representative confocal images of immunofluorescence staining for NSP5-Myc with the indicated organelles or signaling molecules in HeLa cells. Scale bar, 10 µm. Tom20, mitochondrial marker; Calnexin, ER marker; GM130, Golgi marker. g-i NSP5 interacts with RLRs and prevents the interaction of RIG-I and MAVS. g NSP5 interacts with RIG-I and MDA5 but not with MAVS, TBK1, IRF3, or PACT. HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids for 24 h before coimmunoprecipitation. The input and immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. The pcDNA6B vector was used to balance the total amount of DNA in each transfection. Immunoblotting results are representative of two independent experiments. h NSP5 directly binds to RIG-I. Left panel: Coomassie blue staining analysis of the purified RIG-I-Flag and His-NSP5 proteins. Right panel: Co-IP analysis of the in vitro interaction between RIG-I-Flag and His-NSP5. i and j NSP5 impairs the RIG-I–MAVS and RIG-I–TRIM25 interactions. HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids for 24 h. Coimmunoprecipitation and immunoblot analyses were performed with the indicated antibodies. k NSP5 inhibits the phosphorylation of TBK1 and IRF3 induced by SeV infection. HeLa cells were transfected with NSP5-expressing plasmids and subsequently infected with SeV as indicated. The expression of total and phosphorylated (p-) TBK1, total and phosphorylated (p-) IRF3, and NSP5 was detected by immunoblotting. l and m NSP5 prevents the nuclear translocation of IRF3. l Left panel: Confocal microscopic analysis of IRF3 localization in HEK293T cells transfected with an empty vector or NSP5-expressing plasmid for 24 h, followed by SeV infection. Scale bars, 10 μm. Right panel: Quantification analysis of IRF3 nuclear localization (50 cells per sample). m Immunoblot analysis of cytoplasmic and nuclear IRF3. HEK293T cells were transfected with an empty vector or NSP5-expression plasmid. Twenty-four hours later, the cells were infected with SeV for 6 h and the cytoplasmic and nuclear proteins were fractionated. The fractions were immunoblotted with antibodies of IRF3, NSP5, Lamin B1 (nuclear marker), and β-tubulin (cytoplasmic marker). EV empty vector, h hours.