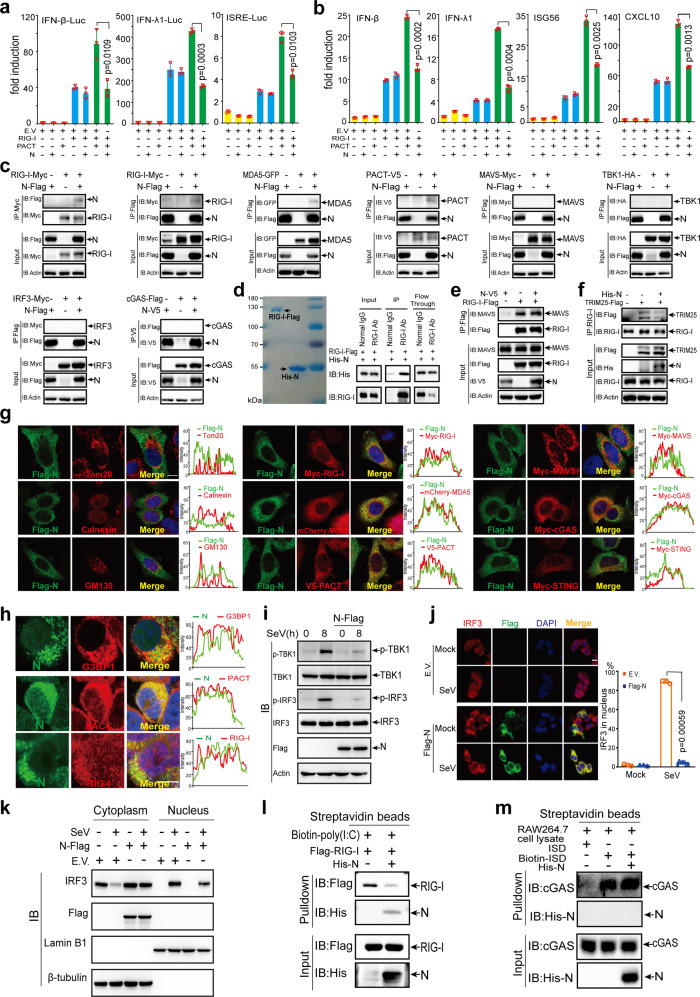
Fig. 6.
N protein prevents PACT-induced RIG-I signaling activation. a and b N protein inhibits PACT-mediated RIG-I signaling activation. IFN-β, IFN-λ1, or ISRE luciferase reporters and protein-expressing plasmids were transfected into HEK293T cells as indicated. Thirty-six hours after transfection (a), dual-luciferase assay was used to measure the luciferase activities. Forty-eight hours after transfection (b), the cells were harvested to analyze the expression of IFN-β, IFN-λ1, ISG56, and CXCL10 using RT-qPCR. c The N protein interacts with RIG-I, MDA5, and PACT rather than with MAVS, TBK1, IRF3, or cGAS. Protein expression plasmids were transfected into HEK293T cells as indicated, 24 h later, the cells were lysed for co-IP. d N protein directly binds to RIG-I. Left panel: Coomassie blue staining analysis of the purified RIG-I-Flag and His-N proteins. Right panel: Co-IP analysis of the in vitro interaction between RIG-I-Flag and His-N. e N protein does not affect RIG-I–MAVS interaction using co-IP assays in HEK293T cells. f N protein disrupts RIG-I–TRIM25 interaction. HEK293T cells were subjected to transfection with the protein expression plasmids as indicated, 24 h later, the cells were lysed for co-IP. g Representative confocal images of N protein with the indicated organelles or signaling molecules in HeLa cells. Scale bar, 10 µm. h Colocalization between endogenous N protein and signaling molecules. HEK293T cells were transfected with pBAC-nCoV-Replicon plasmid to obtain the endogenous expression of viral proteins for 24 h. Immunofluorescence staining was performed with antibodies as indicated. i N protein inhibits the phosphorylation of TBK1 and IRF3 induced by SeV infection. HeLa cells were transfected with empty vector or N protein-expressing plasmids; 16 h later, the cells were subsequently infected with SeV as indicated. The protein levels of total TBK1 and total IRF3 as well as phosphorylated (p-) TBK1, p-IRF3, and N protein were detected by immunoblotting. j and k N protein blocks SeV-induced IRF3 nuclear translocation. j Left panel: Confocal microscopic analysis of IRF3 localization in HEK293T cells transfected with empty vector or expression vector of N protein for 24 h, followed by SeV infection as indicated. Scale bars, 10 μm. Right panel: Quantification analysis of IRF3 nuclear localization (50 cells per sample). k IRF3 expression in the cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions. HEK293T cells were transfected with an empty vector or expression vector of N protein for 24 h followed by SeV infection for 6 h. Afterward, the cells were harvested and separated into cytoplasmic and nuclear portions. Each portion was analyzed by immunoblot for the detection of IRF3, N protein, Lamin B1 (nuclear marker), and β-tubulin (cytoplasmic marker). l N protein prevents poly (I:C) binding to RIG-I. Pulldown analysis of Flag-RIG-I from transfected HEK293T cells binding to poly (I:C) with or without N protein. m N protein does not affect the association between ISD and cGAS. Pulldown analysis of cGAS from RAW264.7 cells binding to ISD with or without the N protein. EV empty vector, h hours.