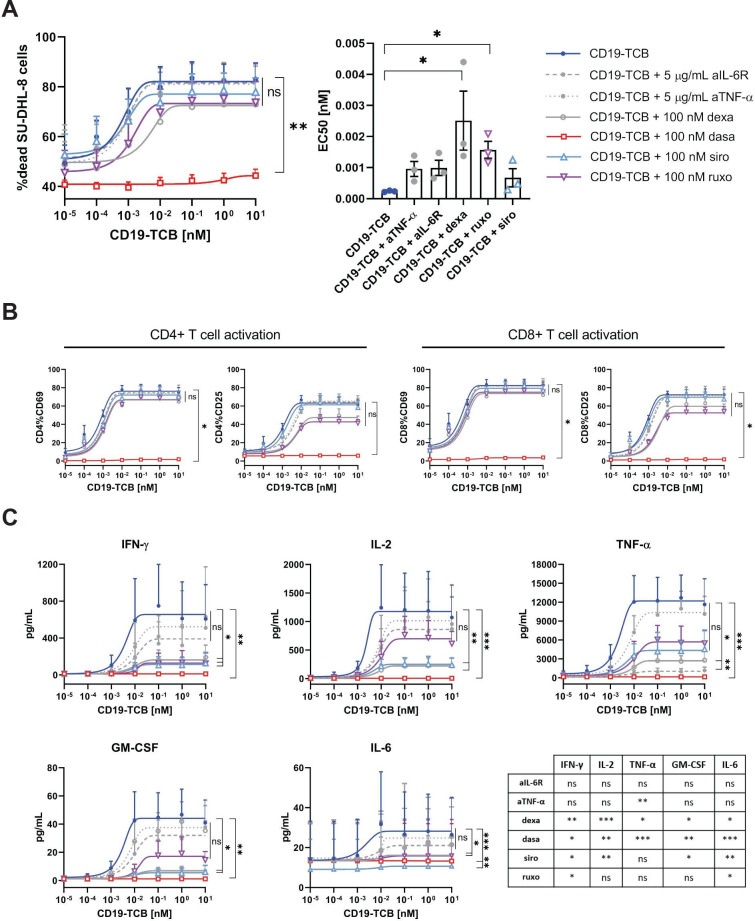
Figure 3.
The effects of mTOR and JAK inhibitors on CD19-TCB induced cytokine release, T cell activation and tumor cell killing are comparable to dexamethasone and more potent than IL-6R and TNF-α blockade in reducing cytokine release. PBMCs were stimulated on CTV labeled SU-DHL-8 tumors cell by CD19-TCB in the presence of 100 nM dasatinib (Src inhibitor), 100 nM sirolimus (mTOR inhibitor), 100 nM ruxolitinib (JAK inhibitor), 100 nM dexamethasone or 5 µg/mL of anti-IL-6R or anti-TNF-α. (A) At assay endpoint (24 hours), cells from technical replicates were pooled and the killing of CTV-labeled SU-DHL-8 cells was measured by flow cytometry by gating on dead NIR-positive cells. The EC50 values of each individual killing curve for n=3 donors are summarized in the bar plot (except for dasatinib, where EC50 values could not be calculated). (B) In addition, the expression of CD69 and CD25 on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells was measured by flow cytometry. (C) Finally, the culture supernatants from technical replicates were pooled and the levels of TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-2 and GM-CSF were measured by Luminex (24 hours). (B–C) Mean of n=3 donors±SEM with *p≤0.05, **p≤0.01, ***p≤0.001 by one-way analysis of variance (Friedman test). For cytokine data, the statistical differences to CD19-TCB treatment are summarized in the table. CTV, Cell Trace Violet; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; PBMCs, peripheral blood mononuclear cells; TCB, T cell bispecific antibody; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.