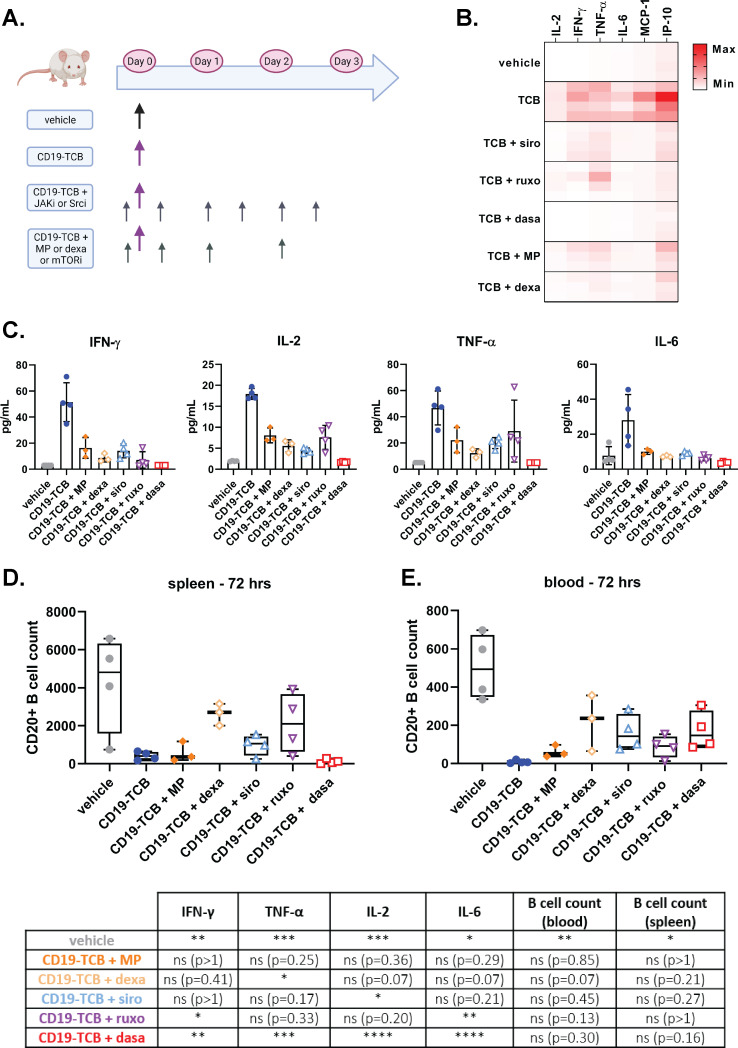
Figure 4.
mTOR and JAK inhibitors mitigate CD19-TCB-induced cytokine release in huNSG mice while not preventing CD19-TCB-induced B cell depletion. (A) In vivo experiment timelines and dosing schedule. Humanized NSG mice were co-treated with 0.5 mg/kg CD19-TCB (intravenously) alone or in combination with 50 mg/kg dasatinib (p.o.), 30 mg/kg ruxolitinib (p.o), 5 mg/kg sirolimus (p.o.), two times 1 mg/kg, 0.5 mg/kg and 0.25 mg/kg dexamethasone (p.o), or two times 10 mg/kg, 5 mg/kg, 2.5 mg/kg methylprednisolone (p.o.). Figure made with BioRender.com. (B, C) Serum was collected from blood 6 hours post infusion with CD19-TCB and cytokine levels were measured by Luminex. The cytokine levels for each mouse were either compared across different treatment groups in a heat map or shown as mean of individual values (bar plots). (D, E). The counts of CD20+ B cells were measured in the spleen and blood collected at termination (72 hours) to assess the effect of kinase inhibitors on CD19-TCB-dependent B cell depletion. (C–E) The statistical differences to CD19-TCB monotherapy treatment are summarized in the table. Mean of n=4 or 3 mice±SD with *p≤0.05, **p≤0.01, ***p≤0.001, ****p≤0.0001 by one-way analysis of variance (Kruskal-Wallis test). IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; IP, interferon gamma-induced protein MP, methylprednisolone; MCP, monocyte chemoattractant protein; p.o., orally; TCB, T cell bispecific antibody; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.