Extended Data Fig 11. Terminal selector provides spatial specificity to nlp-45 expression pattern.
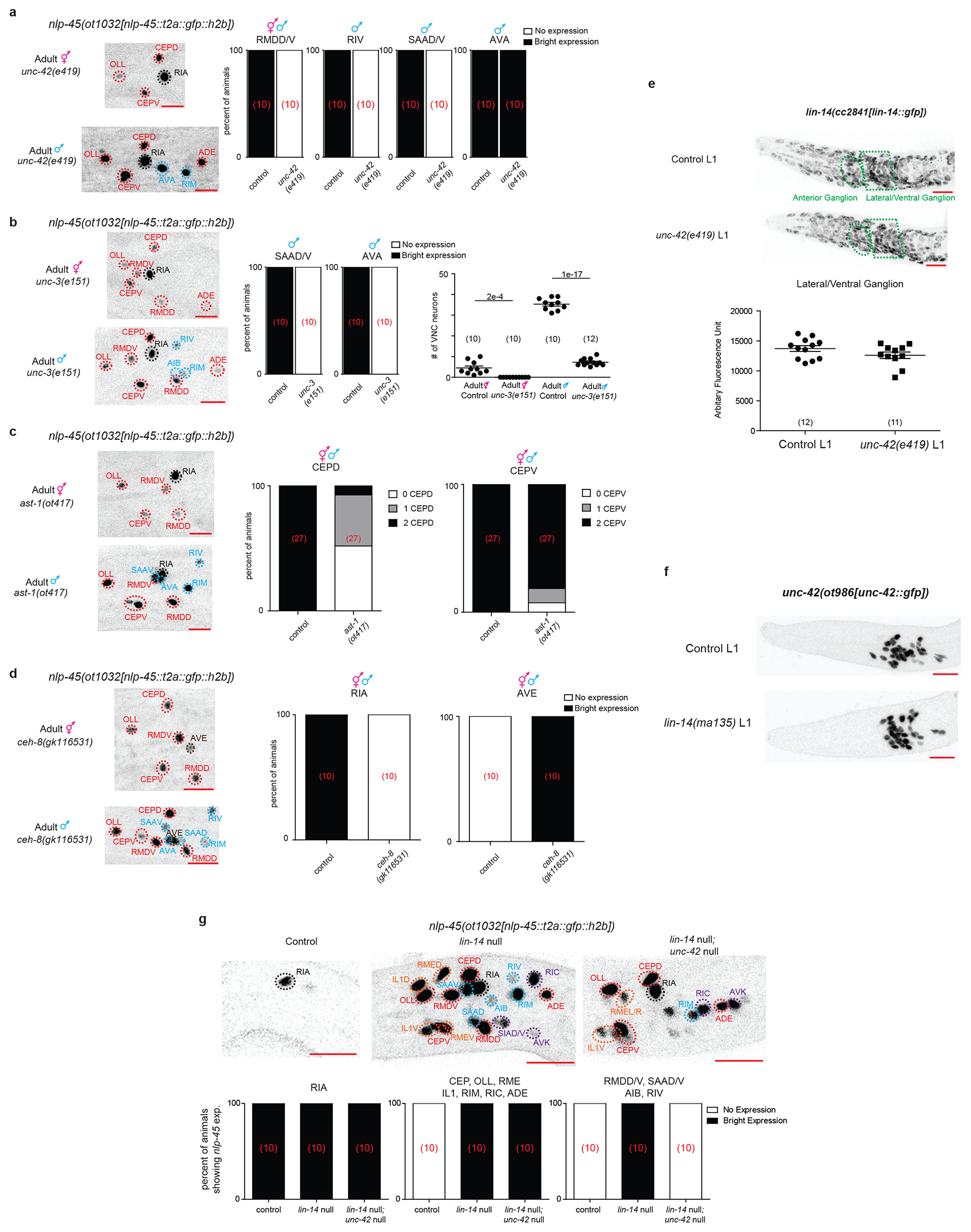
a, Regulation of nlp-45 by cell specific regulator, unc-42. Representative images of adult unc-42(e419) hermaphrodite and male animals are shown on the left while binary quantifications of nlp-45 expression in the RMDD/V, RIV, SAAD/V and AVA neurons are shown on the right (number of animals for each condition is shown in red brackets). nlp-45 expression was lost in all unc-42 expressing neurons with the exception of AVA in unc-42 mutant animals. b, Regulation of nlp-45 by cell specific regulator, unc-3. Representative images of adult unc-3(e151) hermaphrodite and male animals are shown on the left while binary quantifications of nlp-45 expression in the SAAD/V and AVA neurons are shown in the middle (number of animals for each condition is shown in red brackets). The quantification of ventral nerve cord (VNC) motor neurons is shown on the right. n (in bracket) and post-hoc two-sided t-test p values are shown. Each point of the scatter dot plot represents a single animal. nlp-45 expression was lost in unc-3 expressing head neurons (i.e. SAAD/V, AVA) while severely affected in the VNC in unc-3 mutant animals. c, Regulation of nlp-45 by cell specific regulator, ast-1. Representative images of adult ast-1(ot417) hypomorph hermaphrodite and male animals are shown on the left while quantifications of nlp-45 expression in the CEPD and CEPV neurons are shown on the right (number of animals for each condition is shown in red brackets). nlp-45 expression was severely affected in the CEPD neurons and slightly affected in the CEPV neurons in the ast-1 mutant animals. d, Regulation of nlp-45 by cell specific regulator, ceh-8. Representative images of adult ceh-8(gk116531) hermaphrodite and male animals are shown on the left while binary quantifications of nlp-45 expression in the RIA and AVE neurons are shown on the right (number of animals for each condition is shown in red brackets). nlp-45 expression is lost in the RIA neurons and ectopically gained in the AVE neurons in ceh-8 mutant animals. e, Terminal selector (unc-42) does not regulate heterochronic pathway (lin-14). On the left are representative images of L1 lin-14 translational GFP allele worms in control and unc-42(e419) backgrounds. On the right is the quantification of fluorescence intensity in the lateral/ventral ganglion of control vs unc-42(e419) L1 animals. The mean +/− SEM and n (in bracket) are shown for each condition, and each point of the scatter dot plot represents a single animal. f, Heterochronic pathway (lin-14) does not regulate terminal selector (unc-42). Representative images of L1 unc-42 translational GFP allele worms in control and lin-14(ma135) null backgrounds are shown. g, On top are representative images of the nlp-45 expression reporter in control, lin-14(0), and lin-14(0); unc-42(0) L1 animals. On the bottom is are the binary quantifications of nlp-45 expression in different neuronal subtypes in control, lin-14(0), and lin-14(0); unc-42(0) L1 animals (number of animals for each condition is shown in red brackets). nlp-45 showed precocious expression in lin-14, unc-42 double mutants, similar to the lin-14 null mutant alone, except in the neurons (i.e. RMDD/V, SAAD/V) where unc-42 acts as a terminal selector.
