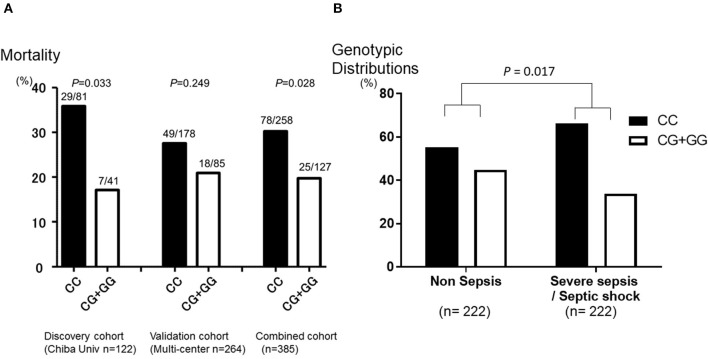
Figure 2.
Mortality and morbidity of severe sepsis in genotype categories of thrombomodulin gene (THBD) single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) rs2239562. (A) The Y-axis of the graph shows the mortality of severe sepsis in the SNPs that is in the promoter region of THBD (−1920*C/G; rs2239562). The patients with the CC genotype of rs2239562 were significantly associated with worse outcome of severe sepsis than the CG + GG genotype of the SNP in the discovery cohort (P = 0.033). The trend was maintained in the validation cohort (P = 0.249), and the association was strengthened in the combined cohort (P = 0.028). (B) The Y-axis of the graph shows the genotypic distributions of the SNP that is in the promoter region of THBD (−1920*C/G; rs2239562) in the patients with severe sepsis and without any evidence of sepsis (non-sepsis). The percentage of patients with the CC genotype of rs2239562 was significantly higher in the SS group than those in the non-sepsis group (P = 0.017). The P values for the SNP were evaluated with the chi-square test on the dominant model analysis with the correlation/trend test.