Figure 2. Methyl-directed MMR.
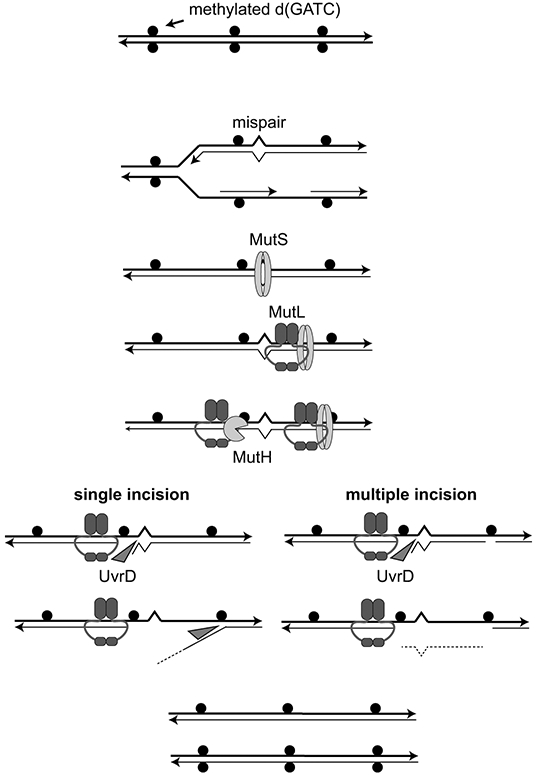
Replication of d(GATC) sites that are methylated on both strands (solid circles) generates hemi-methylated sites that distinguish the parental and daughter strands. Mispairs generated during DNA replication are recognized by the MutS homodimer that then recruits the MutL homodimer. MutL complexes (or MutS-MutL complexes) can then migrate along DNA to activate the MutH single-stranded endonuclease at hemi-methylated d(GATC) either 5’ or 3’ to the mispair. These nicks become entry sites for the recruitment and activation of the UvrD helicase that either generates a single-stranded daughter strand flap (single MutH incision) or a gap in which the mispair-proximal region of the daughter strand is removed (multiple MutH incision). Gap filling by DNA polymerase and DNA ligase completes the repair of the daughter strand.
