Figure 3. In vitro reconstituted eukaryotic MMR reactions.
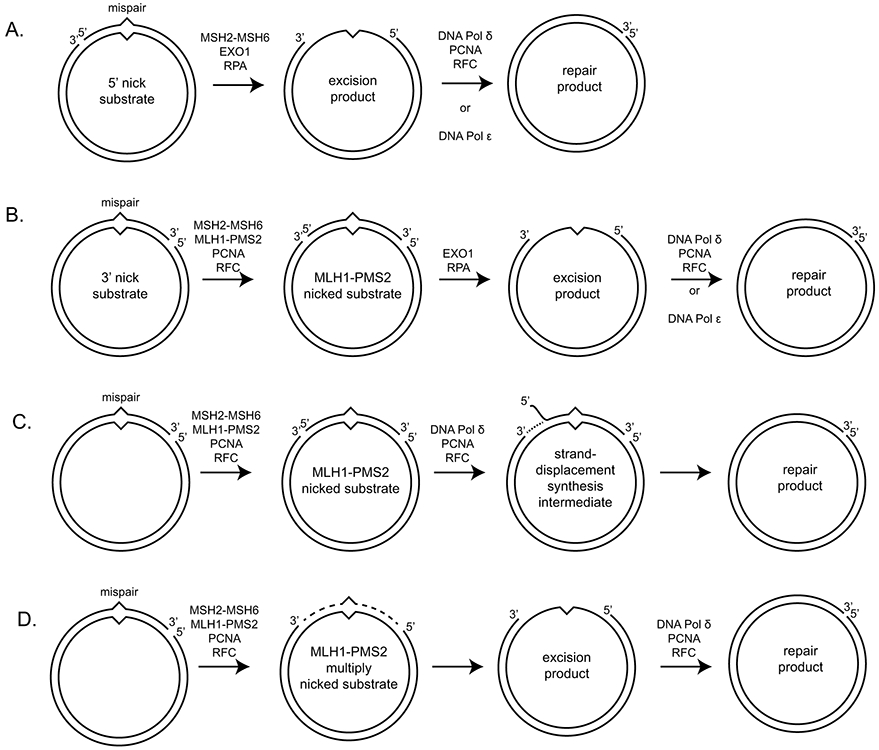
A. EXO1-dependent repair of a mispair-containing substrate with a 5’ nick can proceed by mispair recognition by MSH2-MSH6 and EXO1 recruitment. Nicked strand degradation uses the 5’-3’ exonuclease activity of EXO1. B. EXO1-dependent repair of a substrate with a 3’ nick requires the MLH1-PMS2 endonuclease and its PCNA activator to generate a 5’ nick. Repair then occurs for the 5’ nick containing substrate. C. One possible repair reaction of a 3’ nicked substrate in the absence of EXO1 repair can proceed by generation of a 5’ nick by MLH1-PMS2 followed by strand displacement synthesis by DNA polymerase δ. D. Another possible repair reaction in the absence of EXO1 can proceed by the generation of multiple nicks by MLH1-PMS2 that can give rise to a gap through daughter fragment dissociation, which can then be repaired by gap filling using a DNA polymerase.
