Fig. 3.
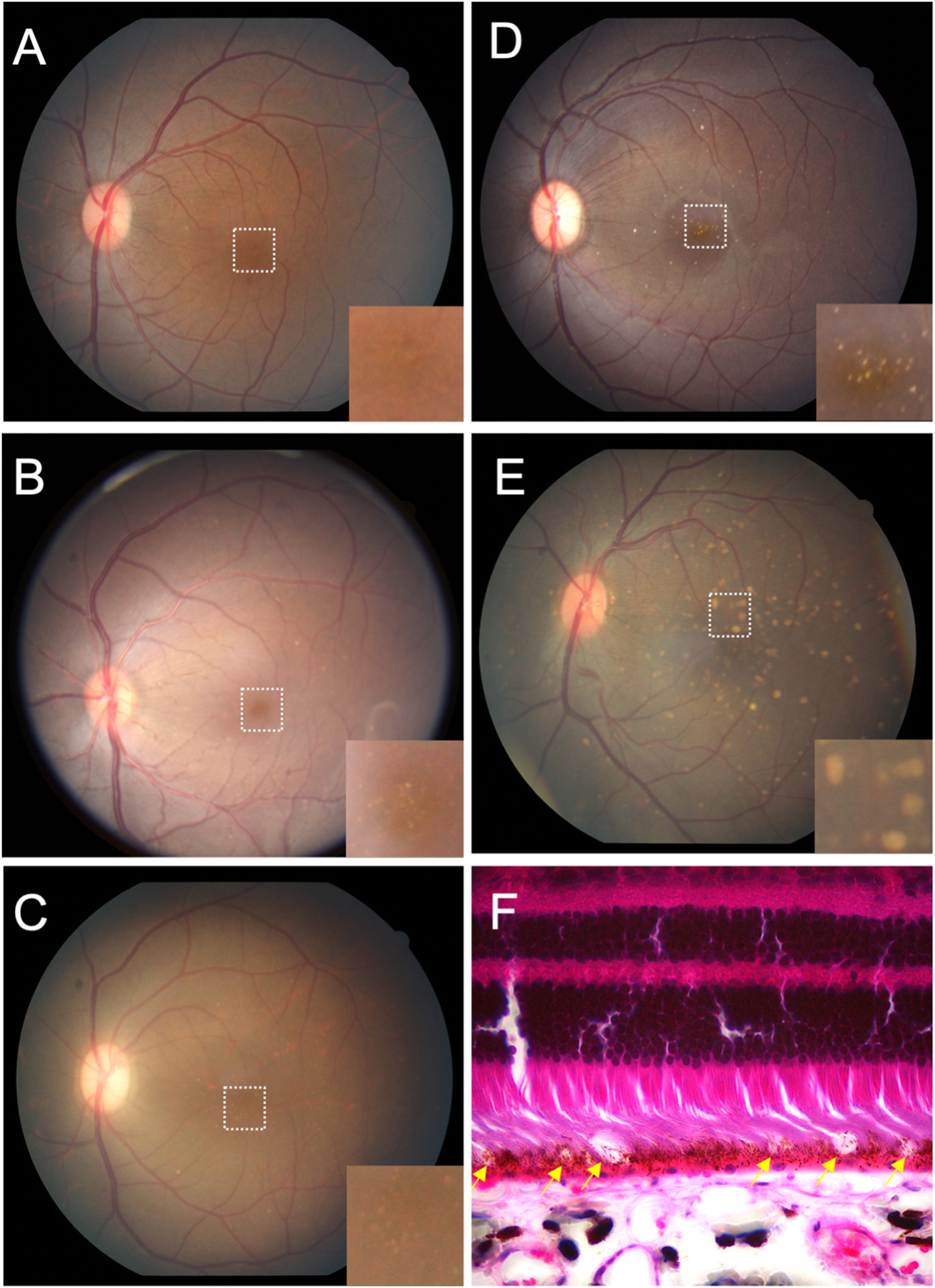
Macular lesions in rhesus macaques.
Grading of macular lesions by clinical examination based on number and area of the posterior pole involved. Inset in A-E is a magnification of the foveal center (dashed box in A) highlighting the lesions.
(A) Color fundus photo Group 0: no punctate macular lesions.
(B) Color fundus photo Group 1: few punctate macular lesions, typically limited to the foveal avascular zone.
(C) Color fundus photo Group 2: moderate punctate macular lesions, typically in the fovea with a few outside the foveal avascular zone.
(D) Color fundus photo Group 3: extensive punctate macular lesions, typically in the fovea and throughout the macula.
(E) Color fundus photo Group 4: soft drusen-like macular lesions.
(F) Hematoxylin and eosin stain of a histological section of a rhesus macaque retina clinically graded with extensive punctate macular lesions. Numerous translucent spheroidal lesions in the outer retina in the region of the photoreceptor outer segments and the retinal pigmented epithelium are seen (yellow arrows). The section is from the macular region as evidenced by multiple rows of nuclei in the retinal ganglion cell layer.
