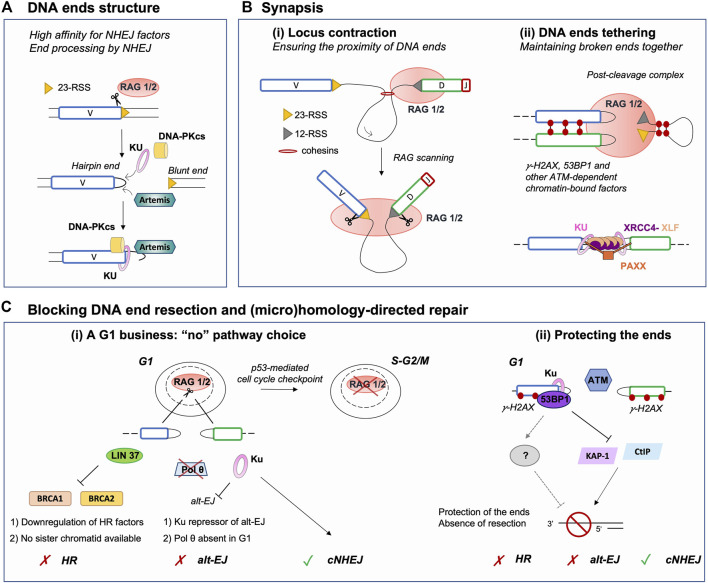
FIGURE 2.
Major parameters restricting DNA repair pathway choice to NHEJ during V(D)J recombination. (A) RAG-induced breakage generates a covalently sealed hairpin end (coding end) and a blunt end (signal end). This facilitates the loading of Ku, which acts as a scaffold for other NHEJ factors, as it has a high affinity for blunt or hairpin sealed ends. In addition, hairpin sealed ends require to be opened by another NHEJ factor Artemis, which renders ends compatible for ligation. Thus, this DNA end topology contributes to the establishment of a NHEJ-prone environment. (B) (i) Upon binding an RSS, RAG scans the adjacent chromatin by a loop extrusion mechanism. Breakage is induced only upon reaching a compatible RSS, ensuring the induction of DSBs in close proximity despite the large size of the immunoglobulin locus. (ii) Following DSB induction, RAG remains bound to DNA ends in a post-cleavage complex (PCC). The PCC together with NHEJ and ATM-dependent chromatin-bound DNA factors (e.g., phosphorylated H2AX and 53BP1) favor DNA ends tethering and stabilization. This likely prevents the search for distant partner DNA ends and channels broken DSB ends to NHEJ for safe repair. (C) (i) V(D)J recombination is a G1-restricted process, as RAG is degraded upon entry in the S phase. In G1, HR cannot operate as pre-replicative cells do not harbor a sister chromatid, used as a template for repair. In addition, several factors required for HR are transcriptionally repressed in G0/G1. Similarly, Pol θ, an important factor for alt-EJ, is poorly expressed in G1 consequently limiting the use of this repair pathway. Furthermore, alt-EJ is blocked by Ku upon binding DNA ends, yet again promoting processing and repair by NHEJ. (ii) Chromatin DSB-response factors γH2AX, 53BP1 and possibly additional downstream effectors contribute to the protection of RAG-DSB ends by blocking the activity of nucleases such as CtIP or acting via transcriptional repressors such as KAP-1. This protection prevents DNA end resection, an essential intermediate step for (micro)homology-directed repair (e.g., alt-EJ, HR, etc.), hence promoting NHEJ. NHEJ: non-homologous end-joining, RSS: Recombination Signal Sequence, Alt-EJ: alternative end-joining, HR: homologous recombination.