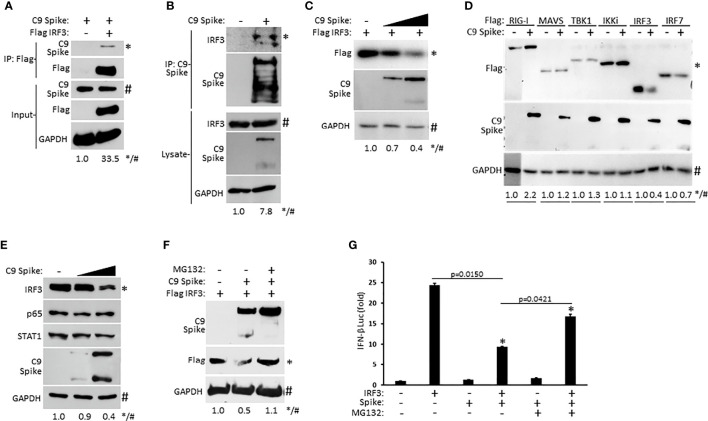
Figure 4.
SARS-CoV-2 Spike interacts with IRF3 and mediates its proteasomal degradation. (A) Co-immunoprecipitation and immunoblot of Flag IRF3 (1 µg) with C9 Spike (1 µg) co-transfected in HEK 293T cells. (B) Immunoprecipitation and immunoblot of transfected C9 Spike (1 µg) with IRF3 in HEK 293T cells treated with MG132 (10 µM) for 4h. (C) Immunoblot analysis of Flag IRF3 (250 ng) co-transfected with C9 Spike (500 ng and 1 μg) in HEK293T cells. (D) Immunoblot analysis of Flag RIG-I, Flag MAVS, Flag TBK1, Flag IKKi, Flag IRF3, and Flag IRF7 (1 µg each) co-transfected with C9 Spike (2 µg) in HEK 293T cells. (E) Immunoblot analysis of IRF3, p65, and STAT1 in HEK 293T cells transfected with C9 Spike (500 ng and 1 µg). (F) Immunoblot analysis of Flag IRF3 (1 µg) co-transfected with C9 Spike (2 µg) in HEK 293T cells and subsequently treated with or without MG132 (10 µM). GAPDH serves as a loading control. (G) IFN-β luciferase reporter assays in HEK 293T cells co-transfected with plasmids encoding IRF3 (500 ng) and C9 Spike (1 µg) followed by MG132 (20 µM) treatment for 4 h. *Indicates p < 0.05 as determined by the student’s t-test. Results are representative of two independent experiments. The relative band intensity (*/#) of co-immunoprecipitated Flag IRF3 in (A), co-immunoprecipitated endogenous IRF3 in (B), Flag IRF3 in (C, F), Flag RIG-I, Flag MAVS, Flag TBK1, Flag IKKi, Flag IRF3 and Flag IRF7 in (D) and endogenous IRF3 in (E) was measured using ImageJ software.