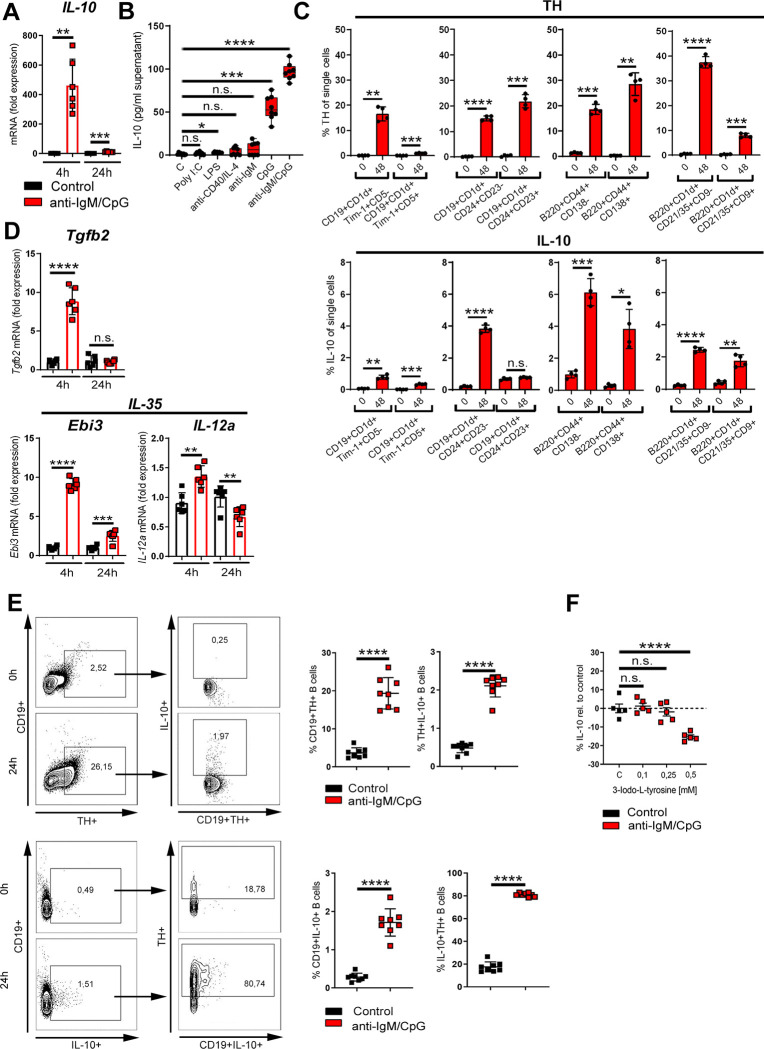
Fig 5. TH up-regulation is associated with IL-10 production.
(A) B cells were activated for 4 h and 24 h with anti-IgM/CpG or left nonactivated. The expression of IL-10 was determined by qRT-PCR (n = 6). (B) B cells were activated with indicated TD or TI stimuli (anti-CD40; Poly I:C, LPS, CpG: 1.25 μg/mL; anti-IgM: 5 μg/mL; IL-4: 1.25ng/mL). Nonactivated B cells were used as controls. The production of IL-10 was measured in the cell culture supernatant by ELISA (n = 8). (C) B cells were activated with anti-IgM/CpG or left untreated. After 48 h, Breg populations and their TH and IL-10 expression were analyzed by flow cytometry and compared to control B cells (0 h) (n = 4). The gating strategy of indicated Breg populations with their characteristic surface markers is available in S8 and S9 Figs. (D) Anti-IgM/CpG-activated B cells or nonactivated cells were cultivated for 4 h or 24 h. The expression of indicated genes was determined by qRT-PCR (n = 6). (E) B cells were activated with anti-IgM/CpG for 24 h or left nonactivated. The expression of CD19+TH+, CD19+IL-10+, TH+IL-10+, and IL10+TH+ B cells was analyzed by flow cytometry (n = 8). One representative dot plot is shown. (F) B cells were treated with different concentrations of the TH inhibitor 3-Iodo-L-tyrosine for 30 min, before activation with anti-IgM/CpG. The production of IL-10 was analyzed in cell supernatants by ELISA (n = 5). B cells from naive DBA/1J mice were used for the experiments. Data are pooled from 3 (E) or 4 (B) experiments. Statistical significance was determined by Student t test (C, E) with Welch correction (A, D) or Brown–Forsythe and Welch 1-way ANOVA tests (B) or ordinary 1-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett multiple comparison test (F). n.s., not significant; *p < 0.5; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001. For underlying data, see S1 Data. ANOVA, analysis of variance; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; IL, interleukin; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; Poly I:C, polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid; qRT-PCR, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; TD, T cell–dependent; TH, tyrosine hydroxylase; TI, T cell–independent.