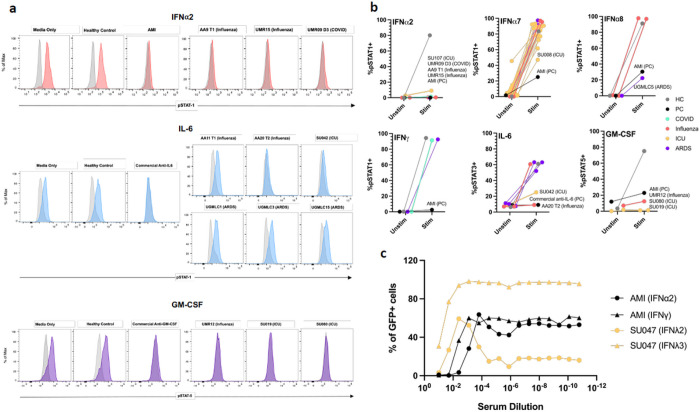
Figure 3. Cell-based cytokine receptor blocking assays.
a Representative fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) plots of IFNα2, IL-6, and GM-CSF signaling assays. Cells were treated with media only; commercial blocking antibody or 10% positive control serum from a patient with atypical mycobacterial infection (AMI); 10% healthy control serum; or 10% test serum. Cells were treated with patient serum or a control in the unstimulated condition (gray) and with both cytokine and patient serum or a control in the stimulated condition (red, blue, purple). b Blocking activity of patient serum on cells in cytokine signaling assays, reported as percentage of pSTAT positive cells in the unstimulated and stimulated condition. Patient sera were from COVID-19 (n = 2), influenza (nGiessen/Marburg = 4, nAthens = 5), Stanford ICU (ninfected = 19, nnon-infected = 2) and ARDS (n = 8) patients. For IFNα2 and IFNα8, results shown represent two independent experiments (Supplementary Fig. 5). Representative healthy controls (HC) and positive controls (PC: commercially available antibody or prototype patient serum with known blocking activity) are also included. c Neutralization activity to IFNα2, IFNγ, IFNλ2 and IFNλ3 in the serum samples of two patients. IFNα2, IFNγ, IFNλ2 and IFNλ3 were incubated with heat-inactivated serum from Donor AMI (positive control) and Donor SU047 (infected Stanford ICU cohort) and added to HAP1 reporter cells. The serum samples were prepared and tested with a 5-fold serial dilution on HAP1 reporter cells. Final concentrations of IFNα2, IFNγ, IFNλ2 and IFNλ3 in the culture were 40 U/ml, 8 U/ml, 1 ng/ml and 1 ng/ml, respectively. The percentages of GFP+ HAP1 reporter cells were evaluated 22–24 hours after the incubation with flow cytometry.