Figure 1. Standard workflow for determining microbiome-disease associations through a case-control study or ML model.
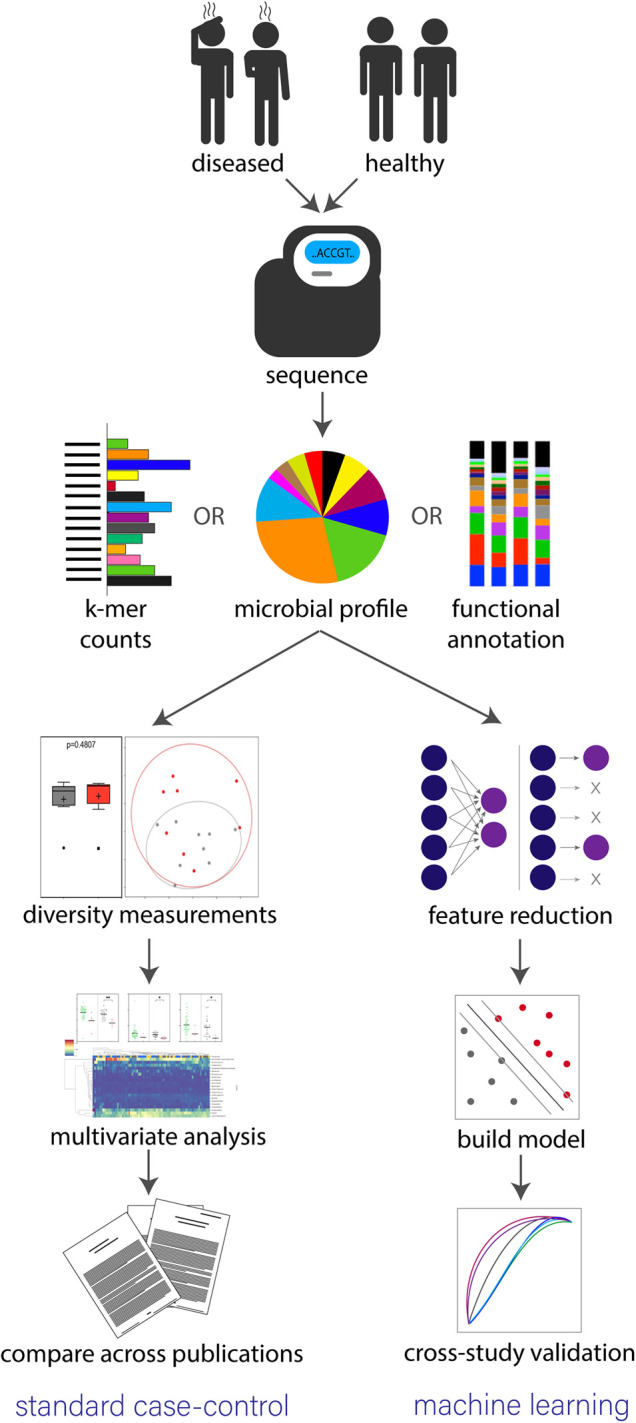
Both approaches begin by separating study participants into diseased and healthy cohorts, collecting samples, then performing high-throughput sequencing. Sequencing is completed through either a WGS or 16S approach then reads are converted to either k-mer counts [21], microbial profiles or functional annotations. In a standard case-control study (left path) alpha diversity, beta diversity and multivariate analysis are used to establish statistically significant differences between the two cohorts. A manual literature review is then performed to determine if findings are consistent across various studies. However, in a standard ML approach, features are extracted from sequence information and a model is constructed to detect trends separating the two groups. Cross-study validation is then performed by calculating accuracy in classification results from other test data sets.
