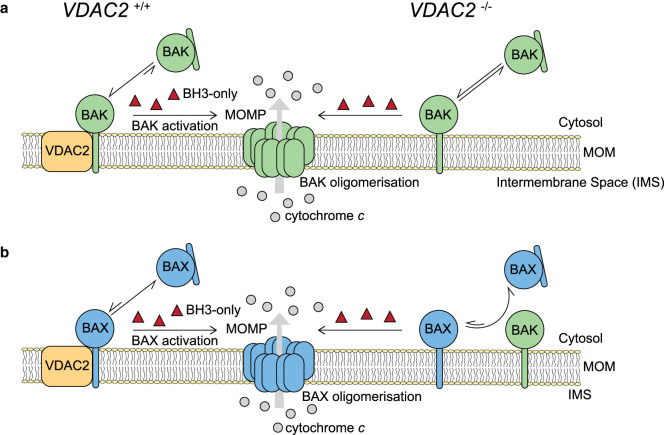
Figure 1. VDAC2 is important for BAK and BAX targeting mitochondria.
The pro-apoptotic effectors BAK and BAX interact with VDAC2 on the mitochondrial outer membrane (MOM) to enable membrane recruitment [24]. Induction of apoptosis by up-regulation of BH3-only proteins activates BAK and BAX regardless of their starting subcellular localisation, and they dissociate from VDAC2 to cause MOM permeabilisation (MOMP) and cytochrome c release from the inter membrane space (IMS) [24,25]. (a) BAK can still migrate to the mitochondria in a VDAC2-deficient (VDAC2−/−) setting [23–26]. (b) However, in the absence of VDAC2, BAX becomes dependent on BAK for its mitochondrial targeting [24,25]. Arrows indicate movement between BAK and BAX localisation and conformation, with arrow length indicating the preference for localisation (smaller is less prominent).