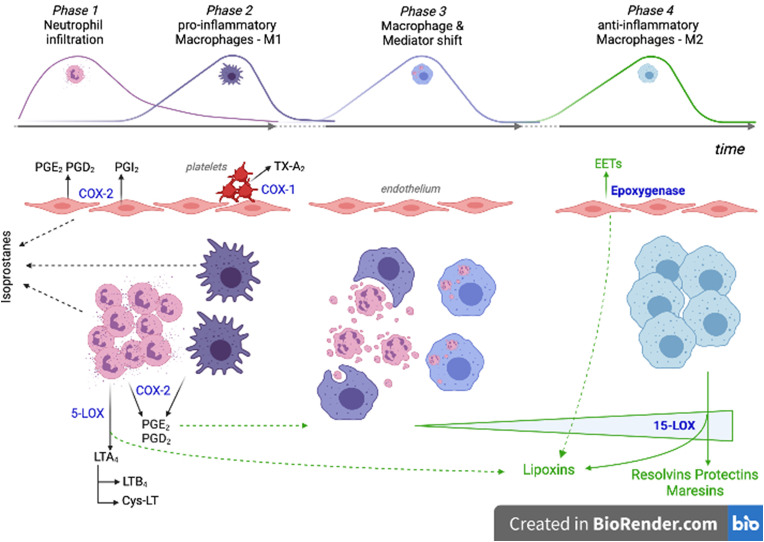
Fig. 4.
Cellular and oxylipin interplay during the evolution of an inflammatory process. Phase 1 and Phase 2: rapid neutrophil and delayed monocyte extravasation in response to cytokines produced by activated immune tissue-resident cells. Pro-inflammatory oxylipins are produced mainly by neutrophils, M1-macrophages, activated endothelial cells and platelets. Phase 3: neutrophil apoptotic bodies and prostaglandins promote the macrophage shift towards a resolution-phase function. Phase 4: inflammation resolution is promoted by increasing production of the specialized pro-resolving mediators. PGE2: prostaglandin E2; PGD2: prostaglandin D2; PGI2: prostacyclin I2; TX-A2: thromboxane A2; LTA4: leukotriene A4; LTB4: leukotriene B4; Cys-LT: cysteine-leukotrienes; EETs: epoxyeicosatrienoic acids; COX-1: cyclooxygenase-1; COX-2: cyclooxygenase-1; 5-LOX: 5-lipoxygenase; 15-LOX: 15-lipoxygenase.