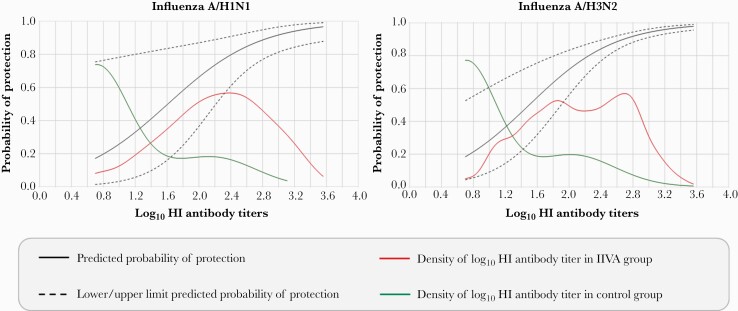
Figure 3.
Probability of protection against reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction–confirmed influenza illness according to log10 hemagglutination inhibition (HI) titer predicted by the Dunning model (per-protocol correlate of protection; HI titer measured at 28 days after last vaccination). The density of log10 HI antibody titer lines show the distribution of postvaccination HI titers in study participants (the proportion of children with titers of the shown level). The graphs begin at a log10 HI antibody titer of 0.7, the assay cutoff level. As expected, a few children in the inactivated quadrivalent influenza vaccine (IIV4) group had very low or very high titers, but most had titers in the mid-range. In contrast, most children in the control group had low HI antibody titers.