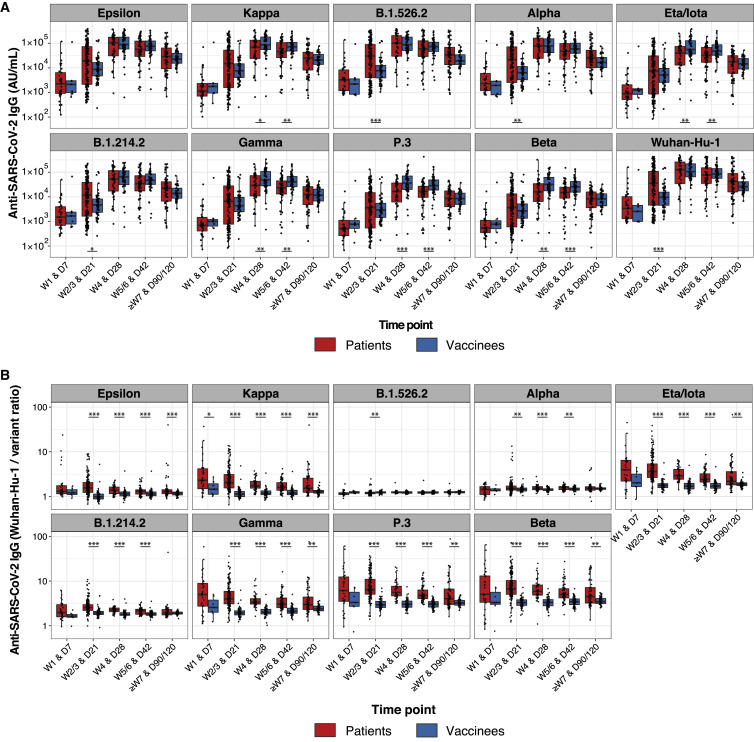
Figure 3.
Greater breadth of IgG binding to SARS-CoV-2 RBD variants following BNT162b2 vaccination compared with infection with Wuhan-Hu-1 SARS-CoV-2
Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Wuhan-Hu-1 and viral variant RBD IgG responses are shown for Stanford individuals who received BNT162b2 vaccination and for Wuhan-Hu-1-infected COVID-19 Stanford patient cohort 1 at different time points after vaccination/COVID-19 symptom onset. Box-whisker plots show the interquartile range as the box and the whisker ends as the most extreme values within 1.5 times the interquartile range below the 25% quantile and above the 75% quantile. Significance between patient and vaccinee groups were tested with two-sided Wilcoxon rank sum test. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001
(A) Anti-RBD IgG concentrations.
(B) Ratios of anti-Wuhan-Hu-1 to variant RBD IgG concentration.