Figure 6.
KLF4 L507A mutant preferentially binds promoter/enhancer of pluripotency-related genes in reprogramming cells
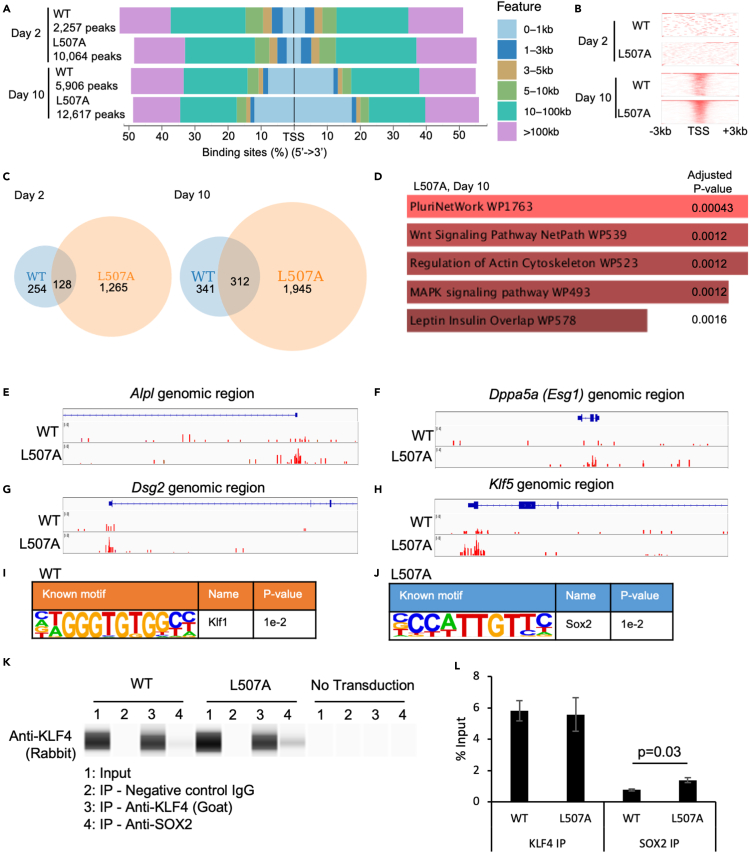
(A) Heat maps of peak distribution and the numbers of peaks from the ChIP-seq data of KLF4.
(B) The distribution of ChIP-seq reads between -3kb and +3kb around TSS.
(C) A Venn diagram of gene sets obtained from the comparison of ChIP-seq data of KLF4 among reprogramming MEF induced by KLF4 WT or L507A on day 2 or 10. Genes that have specific ChIP-seq peaks within 5kb from TSS are categorized in each set. The numbers of the genes in each set are shown.
(D) Wikipathway enrichment analysis was performed on the gene set derived from the sample of L507A on day 10. The top 5 pathways that are enriched with statistically significant are illustrated with the adjusted p values.
(E–H) Mapped ChIP-seq peaks on pluripotency-related genes, Alpl (E), Dppa5 (F), Dsg2 (G), and Klf5 (H). These genes are extracted in the combination with RNA-seq data. Red bars indicate ChIP-seq peaks in each genomic region.
(I and J) Motif discovery analysis was performed on ChIP-seq data of KLF4 in reprogramming MEF induced by KLF4 WT or L507A. Discovered known motifs from WT (I) and L507A (J) were shown with the name of transcription factor and p value.
(K) A typical blot image of capillary Western blot assays on samples co-immunoprecipitated with anti-KLF4 antibody. Reprogramming MEFs infected with SeVdp carrying KLF4 WT or L507A or no transduction for 3 days were used.
(L) Protein abundance was calculated from the data of co-IP assays. Results are mean and SE, n = 3. The p value calculated with a t test was shown based on the comparison between WT and L507A KLF4 conditions.