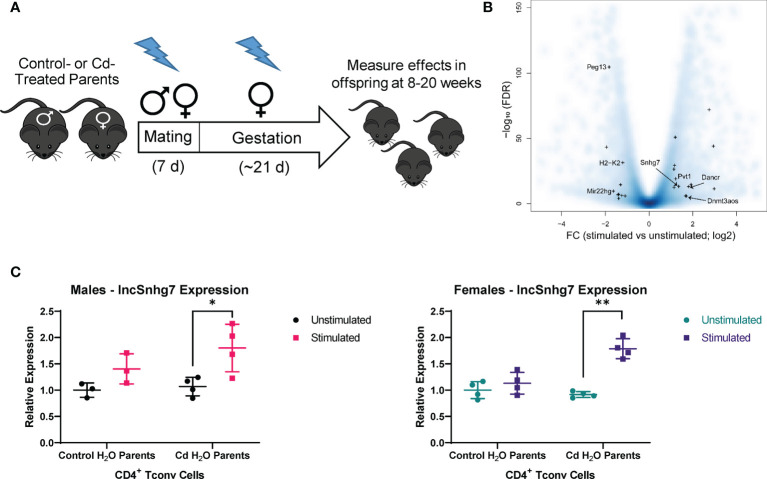
Figure 1.
lncSnhg7 expression is increased in CD4+ T cells with activation. (A) Mice were exposed to Cd during prenatal development. Lightning bolts indicate times where parents are administered CdCl2 (10 ppm) via drinking water. (B) Volcano plot for the comparison of gene expression between unstimulated and stimulated CD4+ T cells. CD4+CD25- T conventional (T conv) cells were isolated from the total splenocytes of control offspring. T conv cells were cultured for 0 or 16 hours in the presence of anti-CD3/CD28 magnetic beads, unstimulated and stimulated, respectively. RNA was isolated and expression was analyzed by RNAseq. Blue background represents all genes (coding and non-coding). “+” indicates lncRNAs detected as differentially expressed in our system (FC > 2 and FDR < 0.01). (C) LncSnhg7 expression is increased in male and female activated CD4+ T cells. CD4+CD25- T conventional (T conv) cells were isolated from control and Cd-exposed offspring and stimulated as in (B) LncSnhg7 expression was evaluated by qPCR. Statistical significance was assessed using one-tailed, paired t-test between stimulated and unstimulated samples. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. n=3-4 per group.