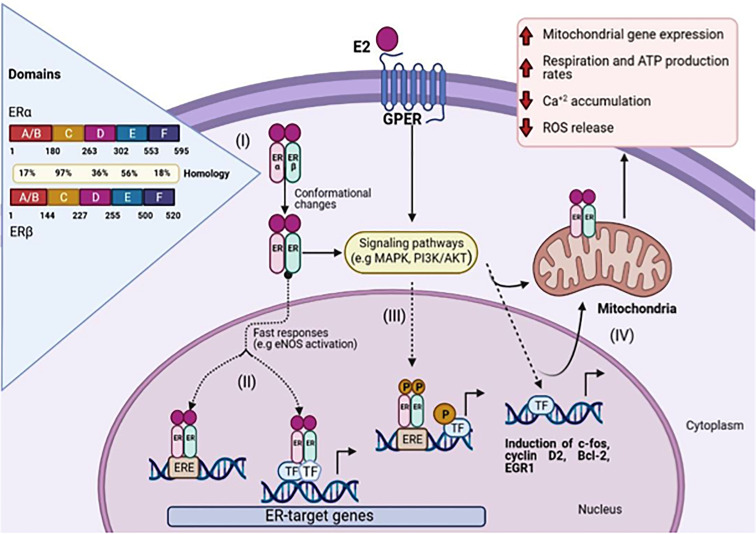
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of 17β-Estradiol induced estrogen receptor-α, β, and GPER signaling. (I) The amino acid sequence position is shown for each domain and the homology between ERα and ERβ. Genomic pathway: (II) The E2/ER complex can bind to estrogen response elements (ERE) within the target gene promoter or regulate gene transcription by interacting with other transcription factors (TF), e.g. AP-1 and Sp1. (III) In addition, E2/ER complex activates signaling transduction pathways, leading to phosphorylation of ER or other bound transcription factors modulating gene expression. (IV) E2 initiated cellular and mitochondrial ER/GPER genomic and non-genomic actions modulate mitochondrial respiration, ATP production, and ROS formation. (Figure created with BioRender.com).