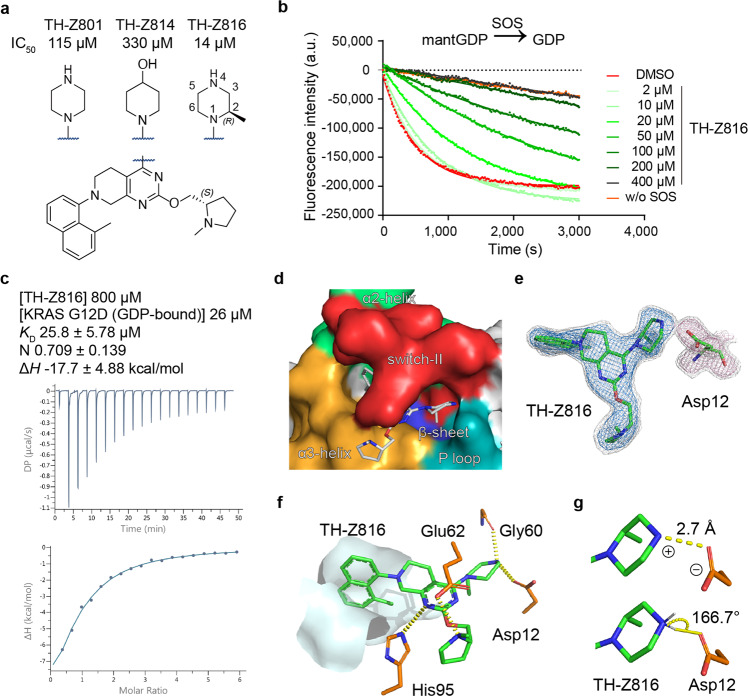
Fig. 1. A piperazine-focused strategy for targeting KRAS(G12D) via salt-bridge interaction.
a Chemical structures of TH-Z801 and TH-Z816 with exposed piperazines, structure of TH-Z814 with non-amine moiety. b Inhibitory activities of TH-Z816 on KRAS(G12D) measured by SOS-catalyzed nucleotide exchange assay with GDP as the incoming nucleotide. c ITC assay of the TH-Z816 (800 μM) and GDP-bound KRAS(G12D) (26 μM). d Crystal structure (PDB ID: 7EW9) of KRAS(G12D) bound to TH-Z816 (white stick). The binding pocket is formed by the α2-helix (green), switch-II (red), α3-helix (orange), P-loop (teal), and the central β-sheet (blue) of KRAS(G12D). e Fo-Fc maps of TH-Z816 (blue mesh, 2.5 σ; gray mesh, 1.5 σ) and Asp12 (pink mesh, 2.5 σ; gray mesh, 1.5 σ). f Interactions between TH-Z816 (green) and surrounding residues (orange). The hydrophobic sub-pocket is shown as a surface diagram. g The ionic bond (upper panel) and hydrogen bond (lower panel) between piperazine and Asp12.