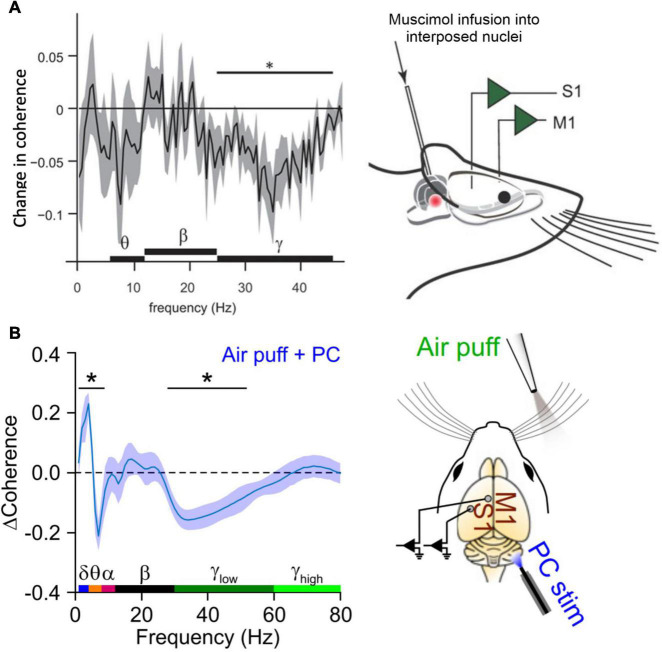
FIGURE 2.
Inactivation of cerebellar output reduces gamma coherence between S1 and M1. (A) In an experiment that involved simultaneous measurements of LFPs in S1 and M1 of awake, head fixed rats, Popa et al. (2013) demonstrated that pharmacological inactivation of the interposed nuclei selectively reduced gamma coherence between S1 and M1. The plot on the left shows a change in coherence relative to the control condition in which the interposed was kept intact. The experimental approach is illustrated on the right (from: Popa et al., 2013). (B) A similar, recent experiment showing that optogenetic inhibition of cerebellar output (via Purkinje cell excitation) significantly reduced the coherence of gamma responses evoked by whisker stimulation. The plot on the left shows estimated effect of Purkinje cell stimulation on coherence between deep layer S1 and superficial layer M1. Theta-range S1–M1 coherence was enhanced with Purkinje cell stimulation (from: Lindeman et al., 2021). *These frequencies were statistically significant (p < 0.05).