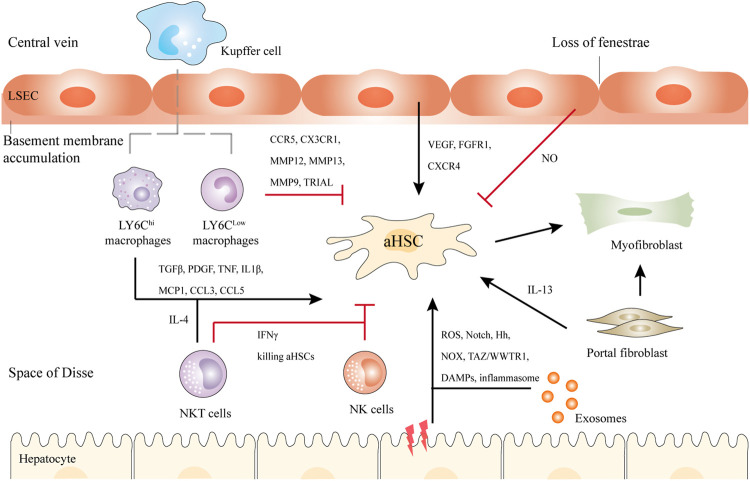
FIGURE 2.
Schematic illustration of the crosstalk between HSCs and Kupffer cells, NK cells, NKT cells, hepatocytes, bone marrow-derived macrophages, and LSECs in liver fibrosis. Briefly, upon liver injury, hepatocytes undergo damage, and inflammatory, releasing DAMPs, exosomes, etc. LY6Chi macrophages activate HSCs by TGFβ, IL1β, and other cytokines, while LY6Clow macrophages show antifibrotic ability via CX3CR1, MMP12, MMP13, etc. NKT cells and NK cells secret IFNγ to kill aHSCs. NKT cells can also activate HSCs through IL-4. In addition, LSECs undergo capillarization and accumulation of basement membranes. They can promote either liver regeneration or fibrosis. Another population of myofibroblasts is the portal fibroblasts, which can also activate HSCs in cholestatic liver. Black and red arrows represent promotion or inhibition of aHSCs respectively.