Figure 5.
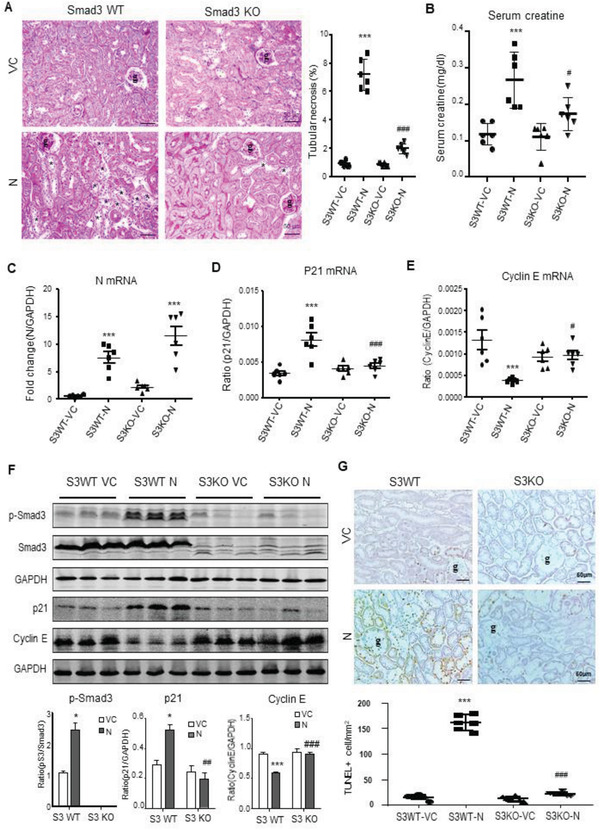
SARS‐CoV‐2 N protein induces AKI via a Smad3‐dependent mechanism. A) PAS staining and semiquantitative analysis of tubular necrosis. B) Serum creatinine. C–E) Real‐time PCR for levels of SARS‐CoV‐2 N, p21, and cyclin E mRNA expression. F) Western blotting for activation of Smad3 signaling (p‐Smad3) and expression of p21 and cyclin E. G) Immunohistochemistry for detecting cell apoptosis by TUNEL‐labeling. Note that mice lacking Smad3 are protected against SARS‐CoV‐2 N‐induced AKI. Each dot represents one mouse and data are expressed as the mean ± SEM for groups of six mice. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 versus Smad3 WT with empty vector control (S3WT‐VC) group; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 versus Smad3 WT with SARS‐CoV‐2 N plasmid (S3WT‐N) group. g, glomerulus; scale bars = 50 µm.
