Figure 1.
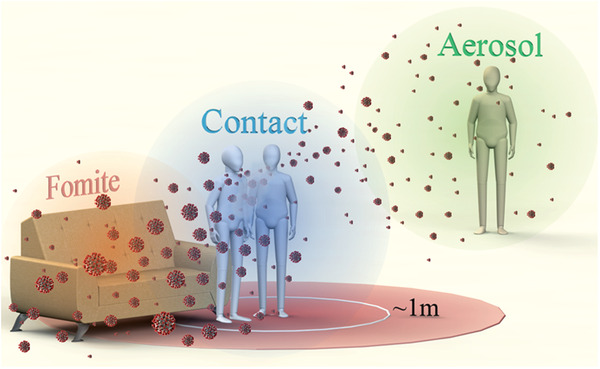
Schematic of three different pathways for the transmission of respiratory diseases. Contact transmission is a result of direct physical contact with an infected person, e.g., handshaking, and the virus is transferred to them.[ 16 , 25 ] Fomite transmission is an indirect and subtle pathway whereby large droplets settle on surface, such as door handles, tabletops, and buttons etc., which then becomes a fomite resource.[ 25 , 26 , 27 ] Aerosol transmission can result in the wide spread of virus with the air flow.
