Figure 1.
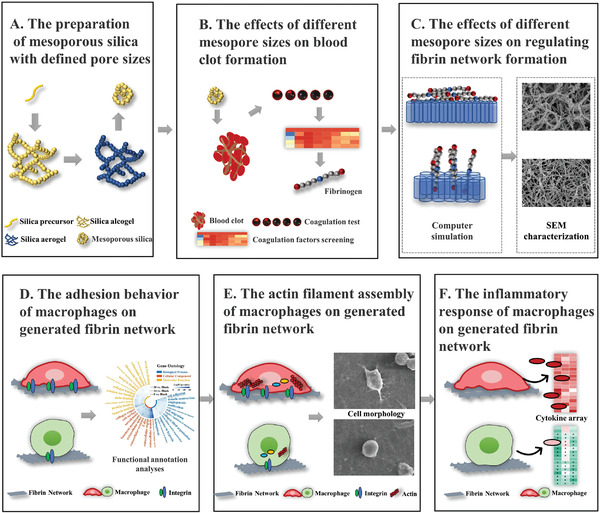
Experimental flow of the study. A) Mesoporous silica with defined pore sizes is prepared using modified sol–gel method. B) Mesopore‐induced clotting time is confirmed in vitro and in vivo, followed by the detection of the key coagulation factor: fibrinogen. C) The effects of mesopore on regulating fibrin network formation and the characteristics of generated fibrin network are investigated using computer simulation, scanning electron microscope (SEM), etc. D) A potential pathway of cell adhesion‐cytoskeleton assembly‐inflammatory response is found using bioinformatic analysis. The adhesion behavior of macrophages on fibrin network is investigated using finite element analysis, RNA‐sequencing (RNA‐seq), real‐time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT‐qPCR), and immunofluorescence. E) The cytoskeleton assembly is then evaluated using RNA‐seq, RT‐qPCR, SEM, and immunofluorescence. F) Inflammatory response of macrophages is eventually evaluated using RNA‐seq, RT‐qPCR, cytokine array, enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and immunofluorescence.
