Figure 4.
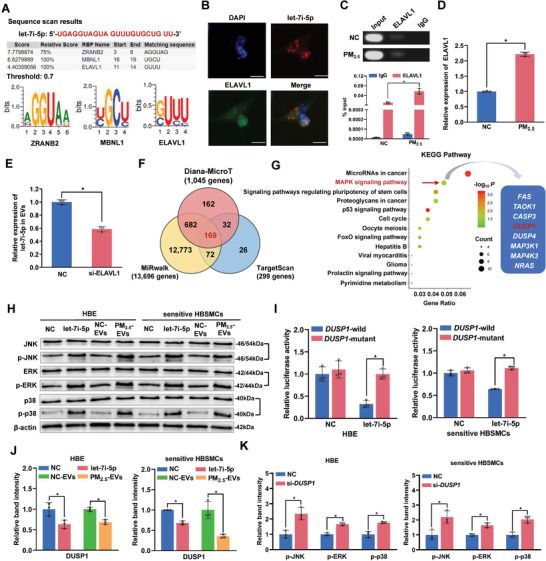
Let‐7i‐5p is packaged into PM2.5‐EVs in an ELAVL1‐dependent manner and regulates the DUSP1 expression level in recipient cells. A) The specific interaction between the let‐7i‐5p sequence and RNA‐binding protein motifs was predicted by RBPDB (threshold value = 0.7). B) Immunofluorescence assessment of let‐7i‐5p (red) and ELAVL1 (green) colocalization in HBE cells. Scale bar, 20 µm. C) Upper panel: image of gel electrophoresis of PCR products from the RIP assay. Lower panel: an RIP assay with an anti‐ELAVL1 antibody or control IgG was performed on PM2.5/NC‐treated HBE cells. The level of let‐7i‐5p in the immunoprecipitates was determined using RT‐qPCR. D) The level of the ELAVL1 mRNA in PM2.5/NC‐treated HBE cells was determined using RT‐qPCR. E) The level of let‐7i‐5p in EVs derived from HBE cells transfected with si‐ELAVL1 was determined using RT‐qPCR. F) The potential target genes containing the let‐7i‐5p seed sequence were predicted using the Diana‐MicroT, MiRwalk and TargetScan databases. G) KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of the 169 target genes. H) The protein levels of MAPK pathway‐related signaling molecules in NC mimic‐, let‐7i‐5p mimic‐, NC‐EVs‐, or PM2.5‐EVs‐treated recipient cells (HBE cells and sensitive HBSMCs) were determined using Western blotting. I) The binding affinity of let‐7i‐5p for DUSP1 was assessed using a dual‐luciferase reporter assay. J) The expression of the DUSP1 protein in NC mimic‐, let‐7i‐5p mimic‐, NC‐EVs, or PM2.5‐EVs‐treated HBE cells (left panel) and sensitive HBSMCs (right panel) was detected using Western blotting. K) The protein levels of MAPK pathway‐related signaling molecules in NC‐ or si‐DUPS1‐transfected HBE cells (left panel) and sensitive HBSMCs (right panel) were determined using Western blotting. Statistical significance was assessed using a two‐tailed Student's t‐test. Values represent means ± SD. * p < 0.05.
