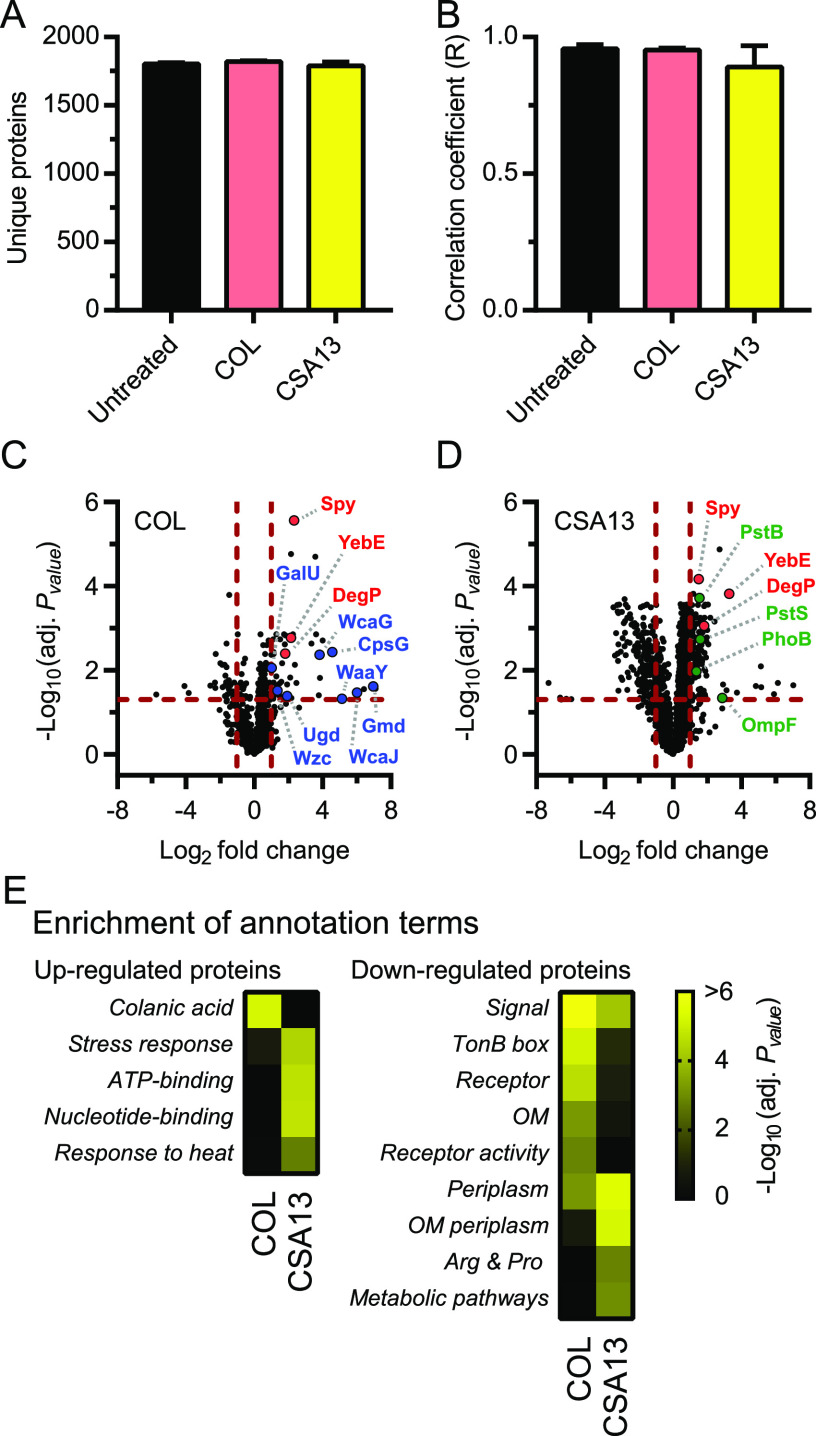
FIG 6.
Proteomic response of E. coli exposed to colistin and CSA13. (A) The number of unique proteins identified for each condition. (B) Correlation coefficient (R) for the number of peptides per protein between the biological replicates of untreated bacteria and bacteria exposed to colistin (COL) or CSA13. Data are represented as means and standard deviations. (C and D) Volcano plots that represent protein expression as means of log2-fold change and −log10 adjusted P values (adj. P value) for bacteria exposed to antibiotics in comparison to untreated controls. Horizontal and vertical dotted red lines indicate adjusted P values less than 0.05 (or −log10 [adj. P value] greater than 1.3) and absolute log2-fold change greater than 1. Some upregulated proteins that are members of the Cpx regulon (in red), involved in colanic acid and LPS biosynthesis (in blue), or members of the PhoB regulon (in green) are highlighted. (E) Annotation terms enriched for proteins significantly up- or downregulated (absolute log2 FC >1 and adj. P value <0.05) following the exposure of E. coli to colistin and CSA13. Adjusted P values of annotation terms associated with a false discovery rate (FDR) value >0.05 for at least one antibiotic are shown. Annotation terms are abbreviated and/or modified for a purpose of presentation (see Data Set S6 for original annotation terms). Data are from 3 independent bacterial cultures for each condition.