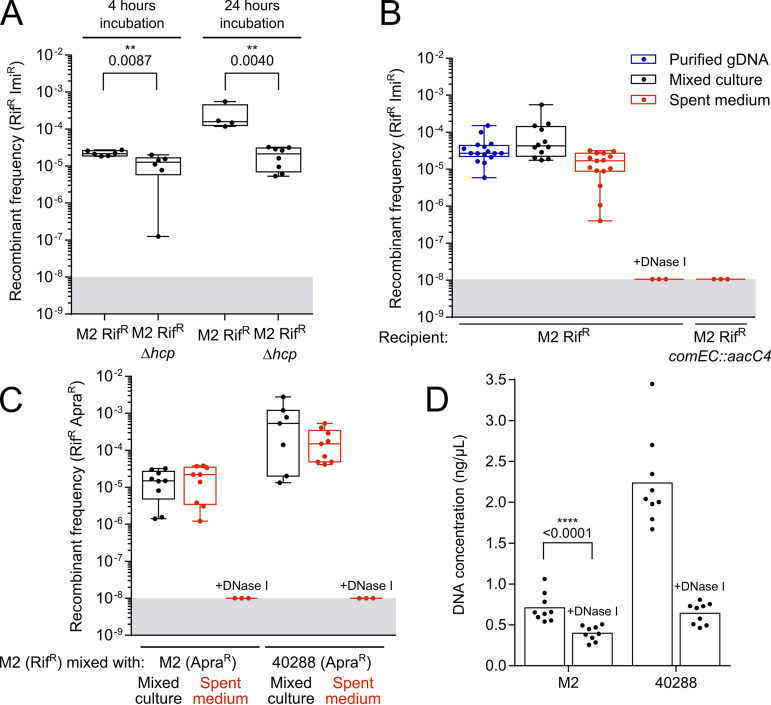
FIG 3.
Contribution of contact-dependent T6SS-killing activity and contact-independent DNA release to the acquisition of the carbapenem resistance in mixed cultures. (A) Contribution of the T6SS to the frequency of recombinants generated in a mixed culture of 40288 and M2 Rifr. 40288 was mixed with the M2 Rifr strain or the M2 Rifr Δhcp mutant, defective for T6SS activity. Imipenem-resistant transformants of the M2 strain were determined after 4 h or 24 h of mixed culture. Transformation frequencies represent the ratio of M2 Rifr Imir CFU over the total count of M2 Rifr CFU. (B) Contribution of contact-independent DNA release by 40288 to the acquisition of the imipenem resistance by M2 in mixed culture. Bacterial suspensions of M2 Rifr at an OD600 of 0.01 were mixed with an equal volume of either genomic DNA extracted from 40288 (at 200 ng/μL), a suspension of 40288 at an OD600 of 0.01, or filtered spent medium of a 4-h culture in tryptone-NaCl medium of 40288. The mixture (2.5 μL) was deposited on the surface of tryptone-NaCl medium and incubated for 6 h at 37°C. Recombinant frequencies represent the ratio of Rifr and Imir CFU over the total. (C) Contact-independent DNA release promotes both intra- and interstrain recombination. The frequency of intrastrain recombinants from M2 Rifr and M2 Aprar strains was determined in mixed culture or when M2 Rifr was exposed to the spent medium of the M2 Aprar strain. To test for interstrain recombination, M2 Rifr was mixed with 40288 Aprar or with the spent medium from that strain. Recombinant frequencies represent the ratio of Rifr and Aprar CFU over the total. (D) Fluorescence-based quantification of DNA present in the spent medium of strains M2 and 40288. Samples treated with DNase I represent the detection limit of the assay (∼0.4 ng). When displayed, P values of statistical analysis were obtained using the nonparametric Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon test (two tailed). The limit of detection (10−8) is indicated by the gray area.