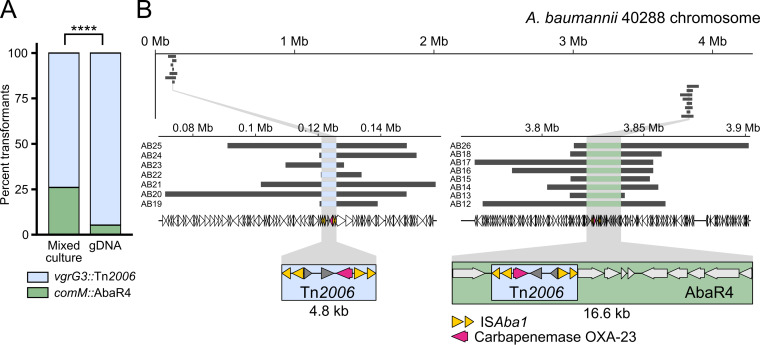
FIG 4.
Genomic analysis of the acquisition of imipenem resistance. (A) PCR-based analysis of the chromosomal location of the Tn2006 transposon and associated blaOXA-23 gene, conferring resistance to imipenem. One hundred Imir and blaOXA-23 PCR-positive CFU from 2 independent transformation assays were analyzed by PCR probing insertion in the comM gene. Statistical significance was calculated using Pearson’s chi-squared test returning a P value of <0.0001 (****). (B) Graphical representation of the chromosome of the 40288 strain (thin black line) and location of the acquired DNA fragments (light gray thick lines) by transformants of the A. nosocomialis strain M2 during mixed culture with 40288. Bottom left and right diagrams represent close-ups of the regions in which the blaOXA-23 gene is acquired as part of the Tn2006 element (blue box) in the vgrG3 gene and as part of the Tn2006 element within the AbaR island (green box) inserted in the comM gene. Acquired regions were determined by sequencing the genomes of imipenem-resistant recombinants of M2 which had acquired blaOXA-23 on a NovaSeq instrument. Variant calling and identification of converted markers (SNPs of 40288 acquired by M2) were used to delineate the acquired regions (see Materials and Methods).