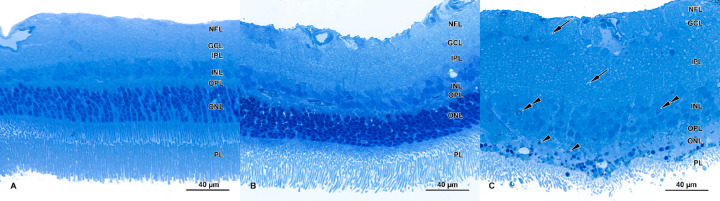
Figure 4.
Effect of blue light exposure on retinal morphology of Brown Norway rats. The rats were exposed to 12 hours of white light (1000 lx) and 12 hours of darkness for 10 days (control, 6 rats), 12 hours of blue light (1000 lx) and 12 hours of darkness for 10 days (long-term, 9 rats), and blue light (1000 lx) for 2 days (acute, 9 rats). Resin-embedded semi-thin sections were stained with toluidine blue. Retinas from control (A) and long-term (B) exposure groups display normal morphology. (C) Retinas from the acute exposure group had deteriorated. Note: loss of nuclei in the outer nuclear layer. Photoreceptors are shrunken and sparser than in the other groups. Signs of apoptosis (chromatin condensation and marginalization) are present in the inner nuclear layer (double arrow). The inner plexiform layer and nerve fiber layer are thicker than in the control group and display vacuolization (arrows). Note the pigment granules scattered in the outer nuclear layer (arrowheads). Samples were visualized with a confocal microscope (LSM700, Zeiss).