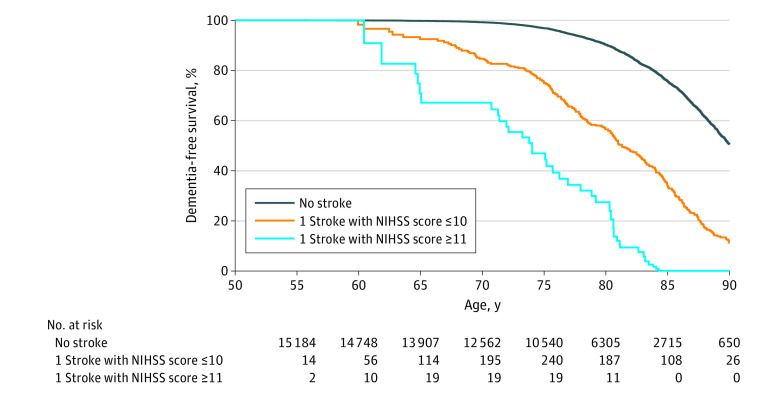
Figure 2. Extended Kaplan-Meier Curves of Dementia by National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) Severity of Incident Ischemic Stroke (N = 15 379).
Extended Kaplan-Meier curves generated using the Simon and Makuch method. Severity of incident ischemic stroke is treated as a time-varying exposure. Consequently, participants do not enter the risk set for ≤10 or ≥11 until the age of incident stroke. Differences in the rates of dementia were statistically significant when comparing participants with stroke to those without stroke (log-rank P < .001; Gehan-Breslow-Wilcoxon P < .001). Rates of dementia among participants >80 years were substantially increased among participants with more severe stroke (NIHSS ≥11) vs without stroke (log-rank trend P < .001; Gehan-Breslow-Wilcoxon trend P < .001). Dementia diagnosis was determined by adjudicated review, telephone interviews, informant interviews, hospitalization records, and death certificates. Only dementia diagnoses with a date more than 1 year poststroke were counted.